Stone, cloth, paper: economic support for village ritual associations
My new film on Gaoluo prompts me to revisit our fieldwork the ritual associations of the Hebei plain—a task further stimulated by the recent reification of these groups under the Intangible Cultural Heritage system. I now wish to outline economic support for such ritual organisations under the successive political regimes of modern times—”breaking through the 1949 barrier”.
First, in this post I expand on some themes from my survey of ritual associations on the Hebei plain; and in a sequel I focus on Gaoluo, where we found a wealth of ritual artefacts to accompany our prolonged fieldwork and discussions with villagers. Both essays are mere samples of the material we collected through the 1990s—please excuse the considerable overlap with many of my previous writings, both on the ritual associations and on Gaoluo. [1]
Introduction
Living traditions of Chinese folk ritual provide a rich source of material artefacts dating back several centuries (cf. China’s hidden century). Still, they are mere snapshots of particular moments: one hopes to be able to augment them by fieldwork on observed ritual practice and the oral accounts of villagers throughout living memory.
In rural China, as everywhere, ritual and cultural life depends on moral and economic support from local communities. Patronage, in cash and in kind, depends on the nature and scale of the enterprise. Occupational family-based groups such as household Daoists and shawm bands (as well as individual intermediaries like spirit mediums) are paid for a particular event such as a funeral, and have successfully adapted to changing patterns of social support in the post-reform era.
In the religious sphere, alongside local temples, the composite term huidaomen (used pejoratively by the Communist state—hui Association, dao “Way”, and men “Gate”) subsumes both ascriptive amateur village-wide devotional associations and voluntary sectarian groups. On the Hebei plain, the two broad categories overlapped (see e.g. our notes on Xiongxian and Xushui counties).
Priding themselves on not accepting payment, ascriptive ritual associations have long relied on recouping their expenses through donations from the village communities whose ritual needs they serve. But whereas support for voluntary sectarian (as well as Catholic) groups remains grounded in enduring faith, the ascriptive associations have faced a particular crisis in the new economic climate since the 1980s.
Temples and temple fairs, ritual associations and the “public building”
Temples have always been an important focus of community life, and in many regions they remain so, such as in south China (Fujian, Jiangxi, Hunan, and so on) and the northwest—although much research there has focused on the imperial legacy rather than modern change.
On the Hebei plain, temples were ubiquitous until the 1950s. Village ritual associations learned from Buddhist or Daoist temple clerics, or from other nearby associations that had done so, at various times since the Ming dynasty; they existed mainly to serve the village temples. But in a long process over the 20th century, temples were destroyed or abandoned; rather few have been rebuilt since the 1980s’ liberalisations, and still fewer have any regular staff apart from a temple-keeper. So the main venue for the reduced calendrical rituals of such villages became the “public building” (guanfangzi: Zhang Zhentao,Yinyuehui, pp.181–204), an inconspicuous building only adorned with god paintings and other ritual artefacts, easily stored away, during calendrical rituals on behalf of the community. Besides the long-term decline of active temples in the region, this may suggest insecurity among village communities through political upheavals.
Villages that have restored their former temples are in a minority, but in such cases the refurbished temples seem to provide a greater focus, visited and tended more often, as in Gaozhuang (Xushui county) and two villages in Xiongxian county, Hanzhuang and Kaikou. Still, their annual ritual calendar remains quite sparse (see my survey, under “Ritual duties”).
Even once we recognise the importance of the “public building”, a major part of the duties of these associations is to supply funeral rituals at the homes of deceased villagers.
Donors’ lists
Alongside the wealth of material artefacts that we found among the Hebei village ritual associations (ritual paintings, ritual manuals, scores, and so on) are donors’ lists (beiwen 碑文), documenting support over the previous year, or for a major initiative. Displayed alongside the god paintings in the ritual building, they proclaim the associations’ support among their community for providing calendrical observances and funerals, symbolising the village’s sacred core. As Zhang Zhentao notes, local terms like beiwen and bushi 布施 (“donating”) remind us of the living connection of these groups with the tradition of supporting Buddhist and Daoist temples.
More ephemerally than the stone steles of temples, the donors’ lists of Hebei village ritual associations are commonly inscribed on cloth; but many are even more perishable, written on paper, pasted on the wall of the ritual building over the New Year’s rituals—when new donations (often in cigarettes and tea) are recorded daily. Thus they might never be documented unless some ethnographer happened to be there to take photos at the time.
Throughout China, paper documents are commonly pasted up announcing temple fairs, temple inaugurations, and particular rituals; some of these may record donors and amounts contributed. Even for weddings and funerals, scribes record gifts. The donors’ lists of the Hebei associations are rather different, recording the names of household heads—thereby establishing them as members of the association not just for particular rituals but throughout the year—and amounts contributed. Since these associations were responsible for performing rituals on behalf of the whole village, their leaders sought donations from virtually every household. Besides a few more affluent patrons, most families could only afford a token contribution.
While village ritual associations were inextricably linked to their local temples, there is no direct transition from the stone steles of the latter to the cloth and paper memorials of the former. Most associations must have made donors’ lists ever since their founding, generally in the Qing dynasty or even the Ming, but alas they don’t survive. Even if they did, we couldn’t make a simple comparison.
For those Hebei temples that have been rebuilt since the 1980s’ liberalisations, we found a rare instance of a stone inscription listing donations on the back of the 1993 stele for the inauguration of the Ancestral Hall to Venerable Mother (Laomu citang) in Gaozhuang, Xushui county—led by the village’s ritual association.
Whatever the material on which such lists are written, the Hebei associations are mostly village-wide public bodies, perhaps encouraging them to openly display both their expenditure and the names of their patrons. Still, many of these groups have sectarian ancestry, so I wonder if such lists have been documented among sectarian groups elsewhere in China—leads welcome.
Lists of expenses
Also often detailed on such lists is the expenditure of the association, justifying the leaders’ probity on behalf of their patrons. Expenses documented include replacing instruments or maintaining them (notably tuning and repairing sheng mouth-organs), commissioning new ritual paintings; buying other equipment (tables, pennants, incense, candles, lanterns, paper, food for banquets); “utility bills” for the ritual building or rehearsal venue (coal for rehearsals, oil for lanterns, electricity); and New Year’s expenses such as firecrackers. For example, again from Gaozhuang is a paper list of expenses from 1995:

Here’s a 1994 list of expenses from Kaikou village (Xiongxian county) for the revival of the temple and its association (Zhang, Yinyuehui, pp.140–43):

Beiwen with written histories
Rather as temple steles from imperial times might also document successive renovations, some donors’ lists include brief histories. Some associations even composed separate histories, such as a 1990 banner from Xin’anzhuang, Renqiu county:

Was this prompted by some interest from county cultural workers, I wonder? It clearly constituted some kind of public declaration; but the preludes of some gongche solfeggio scores of the paraliturgical melodic ensemble, whose readership was limited to the performers themselves, also contain brief histories of the association, like those of Longhua from 1963 and 1980 (for both Longhua and Xin’anzhuang, see under Ritual groups around the Baiyangdian lake).
Intriguingly, the instances that we documented were written since the 1949 revolution. Under state socialism, did political anxieties now prompt ritual associations to proclaim or justify their history, portraying the tradition as “culture”, downplaying religion? Re-reading the brief texts that head some donors’ lists, I find them diplomatic, distancing the associations from sectarian connections, claiming a place within the official discourse long before the Intangible Cultural Heritage. This seems to complement the innocuous appearance of the “public building”, the easily-concealed ritual artefacts, and indeed the growing prevalence of the shengguan instrumental ensemble over the vocal liturgy.
Still, such histories can make a useful starting point as we compile more detailed accounts from villagers’ oral recollections.
Some further examples
Apart from the Gaoluo associations (to be discussed in a separate post), Zhang Zhentao (Yinyuehui, pp.130–50) details donors’ lists from other village groups we visited on the Hebei plain. These include two 1992 paper lists from North Qiaotou in Yixian county (Zhang, Yinyuehui, pp.136–40; see my discussion here)—a donors’ list introduced by a text in praise of the association’s benevolent virtue:

and their list of expenses:

In Xushui county, on our visit to North Liyuan in 1995 we found donors listed on a blackboard:
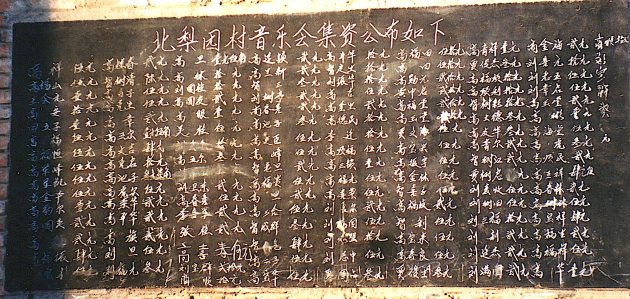
Also under my page on Ritual groups of Xushui is material on the rebuilding of village temples in East Zhangfeng (§8) and Xiefangying (§9). Zhang Zhentao further documents lists from Zhaobeikou on the Baiyangdian lake, and Fuxin in Wen’an county.
Many of these groups were of sectarian ancestry—the North Qiaotou association derived from a Hunyuan sect, for instance. As I suggested above, perhaps this made their public proclamation of charitable virtue still more apposite, counteracting state suspicion of “superstition”.
Summary
Static, silent material artefacts only provide snapshots in the life of these groups. They are most instructive when we can use them in conjunction with fieldwork, helping us connect them to changing social life, filling in the gaps for the intervening periods, learning more about practice and personalities over time, using the frozen material evidence to prompt recollections from villagers, building up a picture of the longer term. This requires prolonged familiarity—as we gained in Gaoluo, subject of the following post.
And to repeat my point yet again, whereas the topic was discovered by musicologists, it belongs firmly within the study of folk religion and society.
[1] For the Hebei ritual associations, see this survey, and many pages under the Gaoluo and Hebei rubrics of the main Menu. Besides my 2004 book Plucking the winds, as well as “Ritual music under Mao and Deng” and “Revival in crisis”, note in particular Zhang Zhentao’s 2002 book Yinyuehui: Jizhong xiangcun lisuzhongde guchuiyueshe 音乐会: 冀中乡村礼俗中的鼓吹乐社. Like his discussions of the “public building” and gongche scores (pp.181–204, 365–407), his chapter on donors’ lists (pp.115–80) is excellent; following perceptive discussions of particular lists, he analyses the material on pp.150–79, including the role of the local gentry in supporting ritual associations, and comparison with the opaque economics of the mercenary shawm bands.
