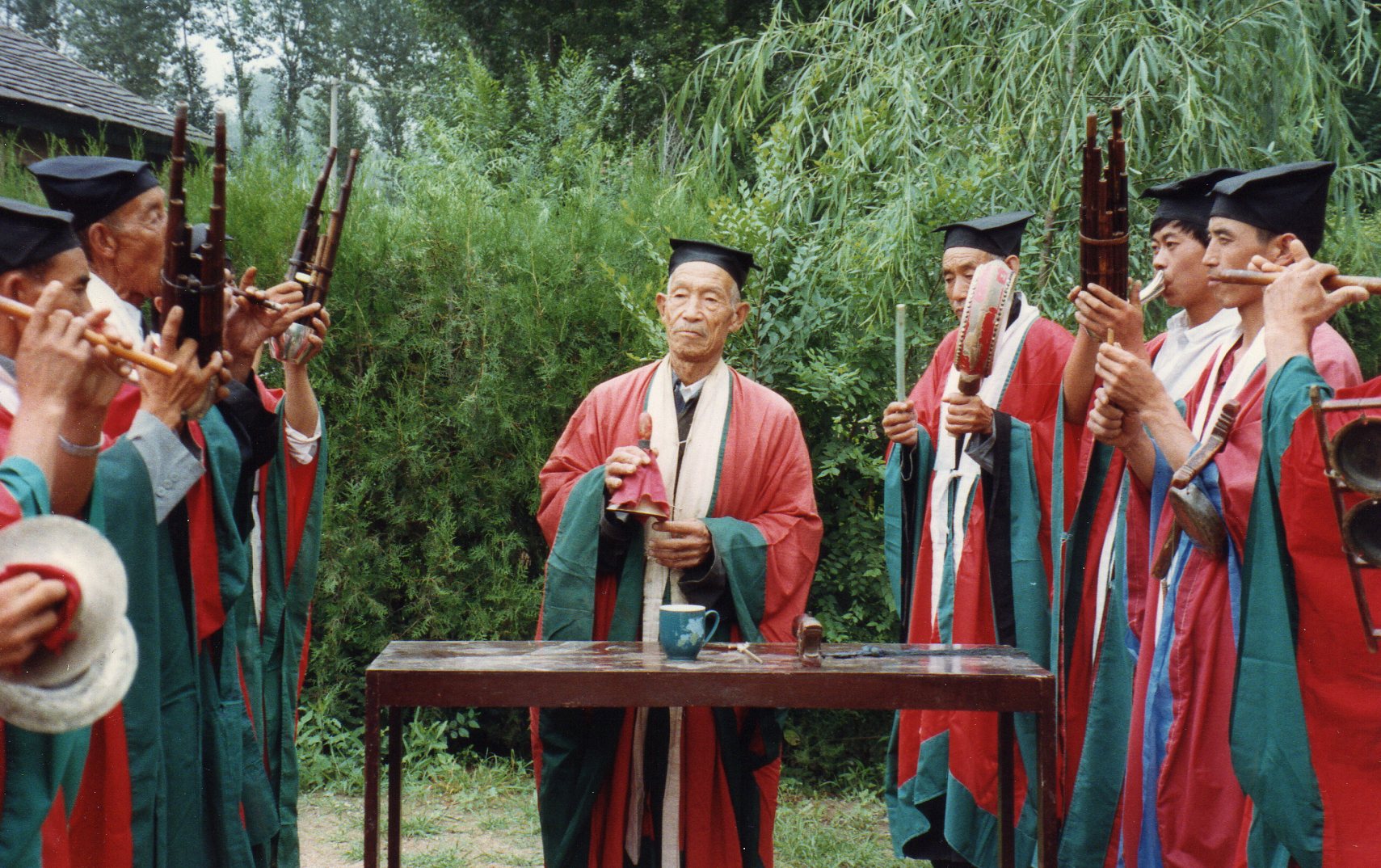
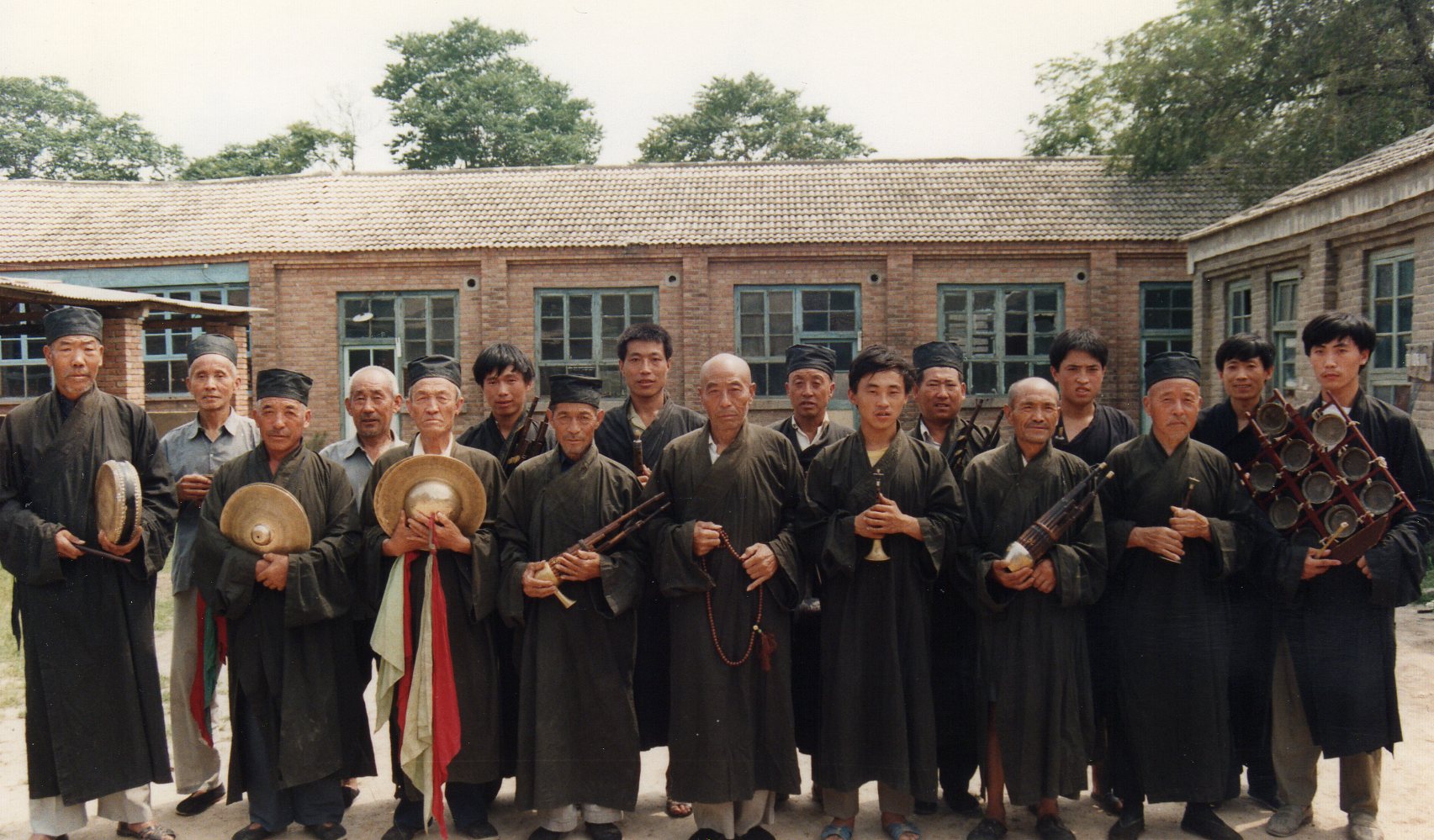
North Shanxi Arts Work Troupe, 1959. Li Qing front row, far right. His four years there (1958–62) were a brief interlude within a lifetime of ritual practice.
For some reason, I found Frank Dikötter’s book The Cultural Revolution far more rewarding than the two previous volumes in his popular trilogy on the Maoist era, The tragedy of Liberation and Mao’s great famine.
Ritual and religious life under Maoism
From the perspective of my own fieldwork on local ritual, there has been no single decade in history where culture has been independent of society— as observed by none other than Confucius and Chairman Mao (see the Coda to my book Plucking the winds), in what may seem like reproaches to the “living fossils” fallacy. To be sure, Gaoluo villagers themselves failed to admit a connection between their ritual association and society:
“The association has nothing to do with politics”
“The association has nothing to do with the Boxers”
“The association has nothing to do with the history of the revolution“.
But all the while they were providing rich material that contradicted their assumptions.
So I would hope that ritual studies can fit into our picture of social change. As I suggest in Appendix 1 of my recent book, scholars of Tang Daoism expect to relate it to the wider history of the period; so why would we who document local ritual groups, whose material derives largely from contemporary fieldwork, not also do so? However deep we probe, the social, economic, and political history of the past century is the air that ritual specialists and their patrons breathe—so what kind of air might scholars breathe by downplaying it?
By failing to study the nuances of the period through which we and our Daoist masters have lived, we ignore precisely the kind of material that historians of earlier periods would die for. Sometimes we fall back on facile clichés about the eternal nature of tradition until the 1940s, and the subsequent destruction of cultural practices (after 1937? 1949? 1966?). All, supposedly, before the untrammelled restoration since the 1980s ushered in an equally timeless and transcendent new Golden Age—unless urban migration and the new pop culture have rendered further study superfluous by destroying tradition further?!
And vice versa, work like this on the changing lives of local communities should also be a contribution to modern historiography—a convenient prism through which to view the “negotiation of identity” (a hoary cliché that I generally avoid!).
With some noble exceptions (such as ter Haar, Ruizendaal and Mueggler), religious life under Maoism is not the strong suit of scholars of religion, but I find it crucial. So I write this partly with a view to reminding those documenting folk ritual in China—and even those who do fieldwork mainly in order to reconstruct the culture of previous ages—that the whole Maoist era is an indispensable part of our background reading and enquiries in the field.
Religion features in many accounts mainly as protest against campaigns (for the 1950s, see The tragedy of Liberation, pp.196–206; Mao’s great famine, pp.227–8), but it’s also worth documenting the “obstinacy” of everyday practice (e.g. The Cultural Revolution, pp.294–6; see also the revival on the eve of the Cultural Revolution, pp.31–2). I belatedly note incidents in places where I did fieldwork innocently in the 1990s, such as the 1966 massacre in Daxing county outside Beijing (p.78).
Maoism
As Dikötter observes (p.119),
Many ordinary people had accepted liberation with a mixture of fear, hope, and resignation. There was widespread relief that the civil war had come to an end. The proclaimed values of the regime, including equality, justice and freedom, were genuinely appealing, and the Part tirelessly trumpeted the New Democracy, a slogan promising the inclusion of all but the most hardened enemies of the regime. Above all, the communists promised each disaffected group what it wanted most: land for the farmers, independence for all minorities, freedom for intellectuals, protection of private property for businessmen, higher living standards for the workers.
Classic studies of local life through the whole Maoist period, a model for detailed local fieldwork, are
- Chan, Madsen, and Unger, Chen village under Mao and Deng (1992) (see also the works of Jonathan Unger, here) and
- the two volume study by Friedman, Pickowicz, and Selden, Chinese village, socialist state (1991) and Revolution, resistance, and reform in village China (2005).
I think also of biographical accounts like Huang Shu-min, The spiral road (1989) and Peter Seybolt, Throwing the emperor from his horse (1996), as well as Jing Jun’s The temple of memories. But on the Maoist period perhaps the most important work of all is that of Guo Yuhua, with her detailed ethnography and critique of “Communist civilisation”.
As a counterbalance to such authors, I like to cite William Hinton (whose Through a glass darkly grinds a leftist axe against the latter), as well as Mobo Gao’s fine ethnography Gao village.
Short of expecting ourselves to read detailed scholarly accounts of the period, such works are important preparation. For our own local studies, apart from works in Western languages, the modern county gazetteers (xianzhi 县志) are an indispensible resource; and I’ve discussed documents on expressive culture here. Note also
- Sebastian Veg (ed.), Popular memories of the Mao era: from critical debate to reassessing history (2019).
A lot has been written about the Cultural Revolution; the period often stands as a simple and misleading soundbite for the whole three decades of Maoism—indeed, ironically, as a shorthand for the first couple of years of extreme violence up to 1968. So since the details of the first seventeen years of the People’s Republic are less well known outside academia, Dikötter’s first two volumes should be more illuminating; in Mao’s great famine individual chapters focusing on topics like agriculture, women, and accidents are well chosen and revealing. But for all the undoubted iniquities that he gruellingly parades, I found the first two books inevitably impersonal, suggesting a lack of empathy that may seem merely to follow a wider pattern in foreign studies of simplistic Commie-bashing.
Dikötter’s study of the famine years around 1960 is part of a growing body of material from both foreign and (laudably) Chinese scholars, on a par with other state-engineered famines like that of Ukraine in the 1930s—as Anne Applebaum’s recent study reminds us. Basic sources include
- Jasper Becker: Hungry ghosts: China’s secret famine (1996)
- Yang Jisheng, Tombstone: the great Chinese famine, 1958–1962 (English translation 2012)
- Wu Wenguang’s memory project
- the works of Xun Zhou
- Ralph A. Thaxton, Catastrophe and contention in rural China: Mao’s Great Leap Forward famine and the origins of righteous resistance in Da Fo village (2008)
- Erik Mueggler, The age of wild ghosts: memory, violence and place in southwest China (2001)
- websites such as China famine 1959–61, and
- China Unofficial Archives.
See also under China: commemorating trauma, Gansu: connecting social trauma and expressive culture (and sequel), with comparative sources under Famine: Ukraine and China.
But the whole period preceding the Chinese “years of difficulty”, to adopt a bitter euphemism, was no picnic either.
The Cultural Revolution
Conversely, we already know more about the Cultural Revolution, but Dikötter explores and augments such material in a communicative way. The Cultural Revolution seems to me less plainly propagandistic. It’s not that the insanities he documents are any more flagrant; rather, perhaps, the account seems more personal. Dikötter effectively meshes central and local perspectives, while showing clearly how the period, often dismissed as a “ten-year disaster” was not one undifferentiated black hole. But as we break up the whole Maoist era into manageable chunks, they bleed into each other—a sadly apt metaphor.
Despite revolutionary fervour being whipped up among naïve youths, cynicism, boredom, and lethargy had set in as early as 1967 (p.165). Any idealism among those students sent down to the countryside to learn from the peasants was short-lived, as they encountered the sheer destitution there (ch.15). As I also learned in Yanggao, severe food shortages continued right until the 1980s.
In the countryside, as organisational chaos spread, market enterprise—which had previously revived in the wake of the famine—also persisted early in the Cultural Revolution; despite a re-imposition of collectivization in 1968, private initiatives were increasingly widespread (pp.225–8). By the “grey years” from 1971, private trade began to expand further. Still many regions were mired in desperate poverty, like Ziyang in south Shaanxi (pp.262–5).
Notwithstanding a late rearguard action (ch.23), Dikötter describes the “silent revolution” in the final years of the Cultural Revolution (chs.21–22) that continued the process of abandonment of the commune system which had come in waves ever since the early 60s. In Henan (pp.274–5) blockades to prevent the private sale of grain were easily evaded:
A weakened state was no longer any match for determined individuals who had honed their skills over many years of hardship. Villagers who had survived the horrors of Mao’s Great Famine were not about to be intimidated by a tax officer hanging about at a roadblock in a conspicuous uniform.
Urban migration, too (a crucial social factor under the 1980s’ reforms), began early. Dikötter even shows an early revival of traditional culture (opera, poetry, story-telling, and so on: p.276).
As in Eastern Europe and the Soviet Union, a hidden, underground, largely invisible society lived in the shadow of the former political system. (p.287)
Still, it’s always worth consulting Mobo Gao’s book Gao village, where with personal experience he gives a more positive, less adversarial picture of Maoism.
Anyway, when the commune system was officially dismantled from 1982, it was largely a fait accompli.
For the Cultural Revolution in Tibet, see here and here; and for a comparison with the Soviet Union under Stalin, see The whisperers.
A case-study
I discussed the whole Maoist era in some detail in both Plucking the winds and Daoist priests of the Li family. In the former, since Gaoluo village lies rather near Beijing and Baoding, the members of its ritual association, themselves active participants, were able to give a rather detailed account of factional warfare and people’s lives through the Cultural Revolution (Plucking the winds, ch.6). But here I’ll just give a few vignettes from my work on the Li family Daoists in Yanggao county of north Shanxi (from my book, ch.6)—who were less actively involved in wider events.
With hindsight, surveying the apparent thriving of religious activities today, the Cultural Revolution period—perhaps even Maoism as a whole—may seem like a blip; but both are crucial elements in the transformation of peoples’ mindsets under the more liberal religious landscape since the reforms of the 1980s.
Household Daoist families in Yanggao had continued performing their liturgy for funerals intermittently for the first fifteen years after Liberation, although the domestic ritual Thanking the Earth was rendered largely obsolete by escalating collectivization from 1953, and temple fairs were silenced.
The immediate precursor of the Cultural Revolution was the Four Cleanups campaign. In many areas of China, “superstitious” artefacts had already been taken off and destroyed in the 1940s as the Communists came to power, but in Yanggao villages Daoist families seem to have kept most of their old ritual manuals until the mid-1960s. Meanwhile Yanggao was still in the grip of ongoing natural disasters.
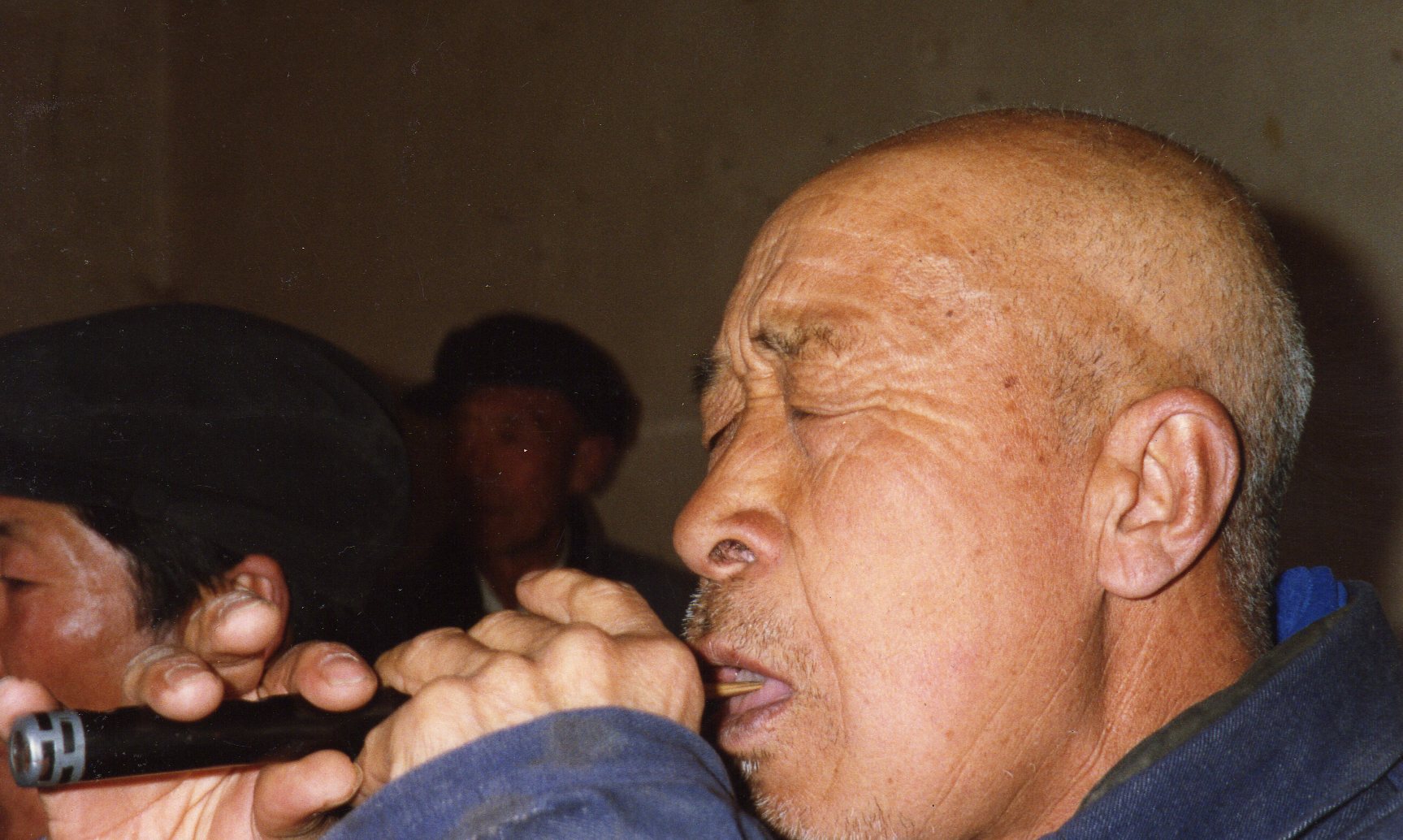
The Four Cleanups must have come as a real shock for kindly Li Qing; having weathered the tribulations of the early 1950s, and then landed a prestigious and secure job in Datong (see photo above), he was even more revered after his return in 1962, and able to practice his beloved ritual again. But so it went for innumerable victims of the “class struggle” system. After the respite of the early 1960s, the mood was now to be grim right until the Cultural Revolution broke out in 1966. Li Qing’s rich-peasant “hat,” though enforced as early as 1948, hadn’t had any great effect until now—not even disqualifying him from joining the prestigious arts-work troupe. But early in the Cultural Revolution he was again classified as a rich peasant.
The Smash the Four Olds campaign from 1966 was the culmination of two decades of measures to limit religious practice. At the same time, campaigns were sporadic.
Following a Four Cleanups re-inspection, late one night in 1966 Li Qing sneaked out to bury his most precious ritual manuals in the sorghum fields just east. Next day, to allay the suspicions of the Red Guards, he burned a large pile of other volumes in his courtyard—he had a large collection of printed volumes and almanacs, not necessarily ritual manuals.
The callow Red Guards paraded Li Qing a few times in a high white dunce’s hat with the characters “ox demon and snake spirit” written on it. But, just like hapless village cadres all over China who were now victimized too, the degree of punishment of so-called landlords and rich peasants depended a lot on their character and reputation. While privately retaining their sympathy for Li Qing, villagers had no choice but to go through the motions of “struggle meetings” dictated from above. Li Qing and his wife bore their sufferings with dignified silence throughout.
When Li Qing’s sensitive sheng mouth-organs were confiscated and deposited in the brigade office, kids messed around with them. Poor peasant Kang Ren was not under suspicion, so he managed to keep his sheng. But here no-one dared ask friends or family to help hide suspect items for them.
Meanwhile in Yang Pagoda, Li Peisen continued to weather the storm. The son of his wife’s younger sister was a Red Guard chief, so they discreetly agreed he would just take off a few scriptures for show—Li Peisen would have chosen decrepit or duplicate volumes that he considered less important.
Li Qing’s son Li Manshan, 21 sui in 1966, had gained an impression of the liturgy before his father left for Datong in 1958, and after he returned in 1962 he had nearly two years of relative freedom to continue learning. After the Four Cleanups campaign of late 1964, though there was no pressure on the children of bad elements to “draw the class line” from their fathers, he felt seriously depressed. At least he didn’t have to join the Red Guards—his status as son of a “black” family disqualified him. One day in 1966, just as the Cultural Revolution was breaking out, Li Manshan found himself in the county-town, and had his photo taken there. He hinted to me that it was virtually designed as a farewell to the world; exhausted by constant labor on the reservoir, with his family’s so-called “rich peasant” status boding ill as an ominous new campaign was brewing up, he could see no future.
In 1960, when Li Manshan was 15 sui, he had “studied Russian for two whole days” at school. Later, when the Red Guards found his notebook with a few Russian words written in it, they confiscated it and cursed him for being a spy. In many parts of China, the innocent possession of a mere scrap of supposedly reactionary material, or a careless comment, could condemn people to long spells in labor camp.
Whereas the neighbouring county of Tianzhen was described as more “barbaric”, the relative peace in Yanggao didn’t mean that Daoists there somehow had any latitude to keep practising. In some parts of rural China traditions were maintained more or less furtively even through the Cultural Revolution, but here the Daoists were forced into total inactivity from 1964 to 1978. Daoist arts went into hibernation. Li Qing’s family, with their black class label, suffered more than other Daoists, but everyone was pretty desperate.
Villagers weren’t becoming any less “superstitious”. Public rituals might be impossible, but there was still a clandestine demand for determining the date, under cover of darkness. For a daring couplet pasted up in the period to satirize the poverty of their conditions, see here.
In 1967 Li Manshan was among a group of Upper Liangyuan team members who had to walk to the commune seat of Greater Quanshan, in the hills to the west, to take part in one of a series of huge public criticism meetings of the disgraced Party Secretary of Yanggao county before his incarceration. By now this model commune had been eclipsed by Dazhai further south in Shanxi, but it still had to host visiting delegations and mass meetings. Ten thousand people from five communes attended the struggle session, all arriving on foot. Although Li Manshan was a “rich peasant,” he had no choice but to go, or else people would accuse him of being counter-revolutionary.
The Sojourn of Educated Youth
Shoulders unable to carry, hands unable to grasp, soft and sensitive skin…
Coming across this phrase in 2013 as I made inept attempts to help Li Manshan with the autumn harvest, I thought it might have been coined to parody my efforts. Rather, it is a standard expression used to describe the travails of urban “educated youth” in performing physical labour after being sent down from the cities to the countryside in the Cultural Revolution to “learn from the peasants.” The experience was a rude shock for such groups all over China; brought up in relatively comfortable urban schools to believe in the benefits of socialism, and often protected from understanding the tribulations of their own parents, they were now confronted not just by the harshness of physical labour, but by medieval poverty (see also my Shaanbei book, p.9).
From 1967, large groups of secondary school students were sent down to live in many Yanggao villages. Over thirty stayed in Upper Liangyuan for a year or so, but Li Manshan had no contact with them. A group from one Beijing school descended on Golden Noble’s village of Houying in 1967, then another batch the following year; most managed to leave around 1972. Golden Noble’s cousin married one of them in 1971, condemning her to rural life; desperate to escape, she eventually divorced him, getting back to Beijing around 1980.
These groups of students brought their musical and acting skills to some villages where they were based, performing revolutionary songs and model operas to dour bemused peasants. Li Manshan never heard them sing or play, but in nearby Shizitun Older Li Bin learned the modern system of cipher notation from educated youth billeted there.
Just when convulsions seemed to have eased, Li Qing’s rich-peasant status was re-imposed in the Cleanse the Class Ranks campaign of 1968. If there had been a certain basis for the original classification around 1949, by now—in a ravaged countryside where everyone was virtually destitute—the label caused his fellow villagers bitter mirth, who ribbed him, “Call yourself a rich peasant?!” After the chaotic first couple of years, things quietened down by around 1969, but there was always tension. As Li Manshan recalls, “We just sat around at home, but we could never feel at peace”—always fearing a knock at the door.
Life Goes On
Even then, life was not entirely about campaigns. Having had four children by 1954, Li Qing and his wife had been separated for four years while Li Qing was in the Datong troupe, but in 1967 they had a third daughter, and then in 1969 a third son, Li Yunshan (known as Third Tiger), twenty-three years Li Manshan’s junior. For the lovely little wooden folding stool that Li Manshan made in the late 1960s, see here.
Then, in the winter cold late in 1971, Li Manshan married, aged twenty-six sui. The new couple lived in Li Qing’s courtyard complex, part of which had been allocated to another family after land reform. In the Cultural Revolution Li Qing “bought” it back, but village cadres accused him of illegal trading, and confiscated it again. Anyway, from 1948 right through till 1980 their conditions were cramped. In 1972 Li Manshan had to spend another six months away laboring on the reservoir project, only returning for the autumn harvest. The couple’s oldest daughter was born in 1973. That year Li Qing and his wife took their youngest son Third Tiger, five sui, into town for a group photo—now nowhere to be found. Around that time Li Qing managed to get his mother’s ashes back from Inner Mongolia, reburying her with his father’s coffin in the family graves outside Upper Liangyuan—though without any ceremony, of course.
All this was around the time of the campaigns to Study Lei Feng and Criticize Lin Biao and Confucius. The latter, prompted by the mysterious 1971 death of Lin Biao in a plane crash in Mongolia, caused major convulsions in Party and army ranks, but Li Manshan has only the vaguest memories of these campaigns.
Whereas through the 1950s and 60s the Party had somehow managed to whip up enthusiasm for further campaigns despite constant abuses, by the 1970s people had thoroughly lost their appetite for the constantly changing directions of policy. Indeed, in Yanggao people were largely unaware of the machinations at the heart of the Party in distant Beijing.
I would gladly qualify all this gloom with reminders of the benefits of Maoism such as are offered by apologists like Bill Hinton and Mobo Gao. But I can find no-one in Yanggao who can think of any. There were some harbingers of reform, like a certain freeing up of markets in 1972. Education too was expanding again. A sporadic supply of electricity eventually reached villages like Upper Liangyuan by the mid-1970s. Before that people used kerosene lamps, but they slept soon after it got dark—except, of course, when there were rituals to perform. The electricity supply in the countryside remains unreliable.
By the 1970s the national population was increasing rapidly, but that of villages like Upper Liangyuan grew little. Under Maoism there was hardly any new house building in Yanggao; by the 1970s, over ninety percent of houses in the county had been built before 1937. By the mid-1970s a few villagers managed to buy watches; even by the end of the decade only a few cadres enjoyed the luxury of riding bicycles.
Traditional culture was still on hold. Without the benefit of hindsight, there was no end in sight to the depression of the commune system. And people—not just the Li family, but the whole population—were still seriously hungry.
* * *
For local Daoist ritual, I must stress that none of this obviates the need for the study of early textual history of ritual manuals, which should continue to play a major role. However, the life stories of Daoists (and all kinds of religious practitioners) are just as important for the modern era as for the imperial period—but with careful and sensitive fieldwork they are much more available. And they can not only clarify aspects of textual transmission, but also (more crucially?) illuminate the changing performance of ritual. So it seems to me that whether sinologists and ethnographers like it or not, our subject has to embrace both early and contemporary periods. At the same time, modern historians may even find our discussions of ritual life in living times to be of some relevance to wider histories.
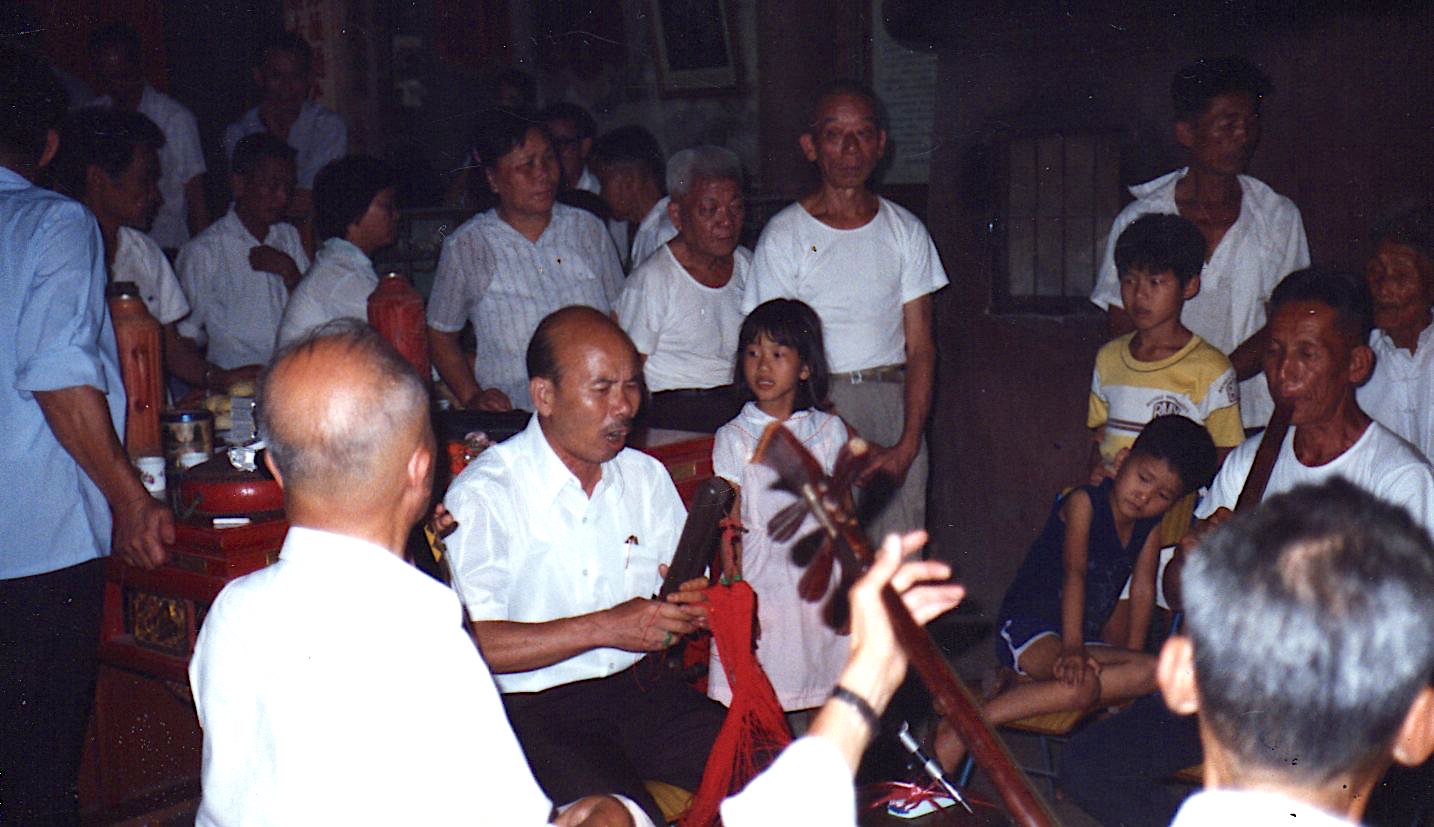
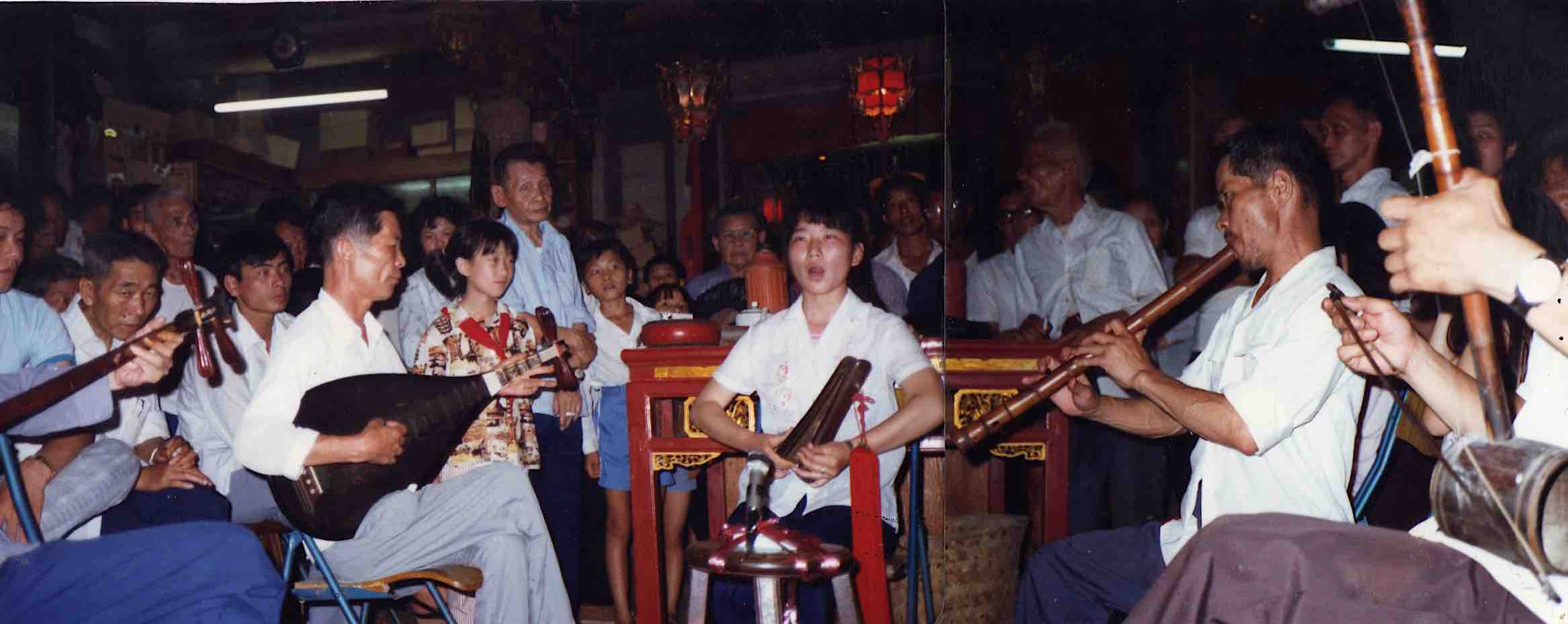




























 Apart from the usual suspects like the Bhagavad gita, Eliade, Castaneda, Jung,
Apart from the usual suspects like the Bhagavad gita, Eliade, Castaneda, Jung,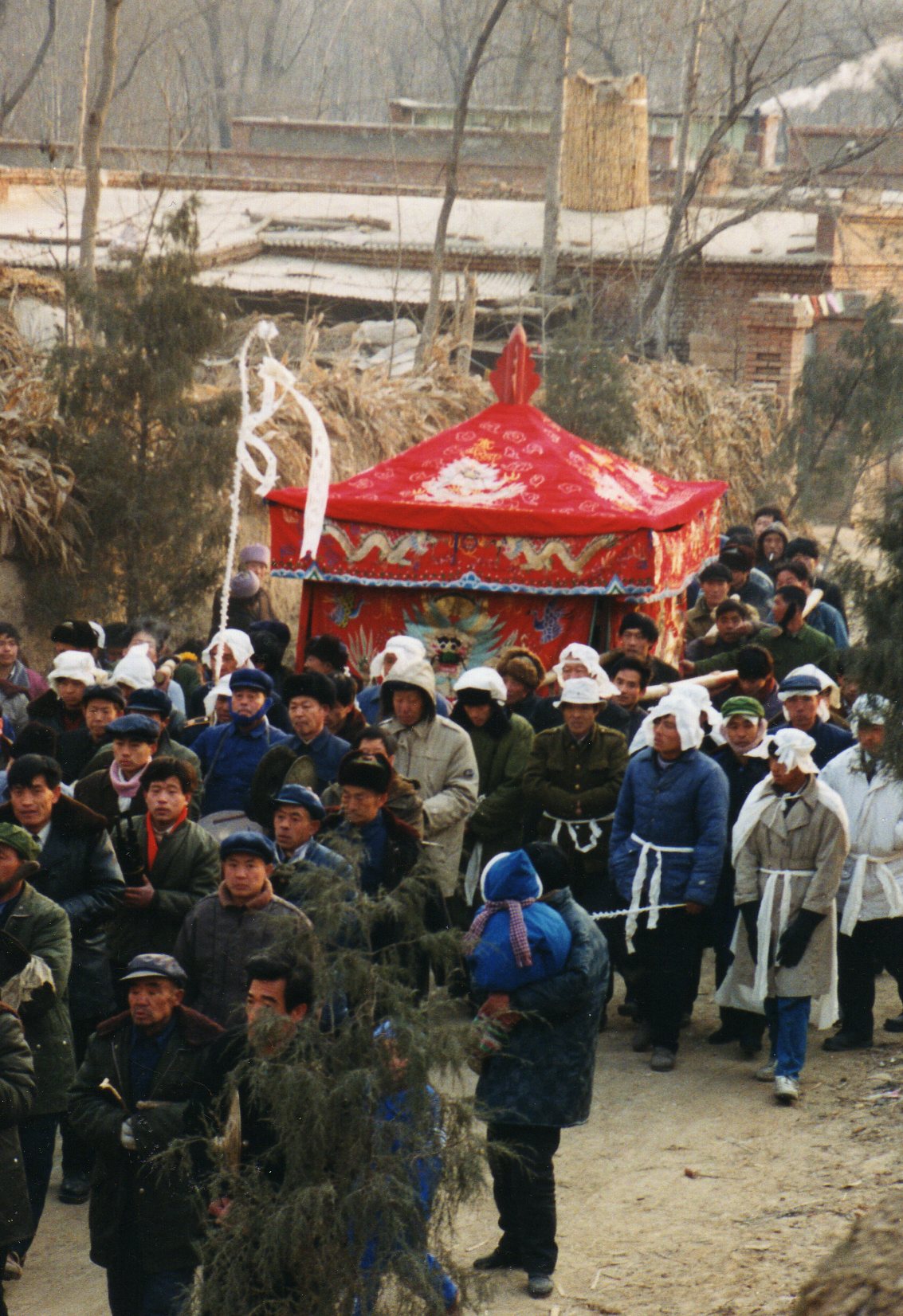 
 Still, even photos of ritual practice remain silent and immobile. Given that ritual is
Still, even photos of ritual practice remain silent and immobile. Given that ritual is 
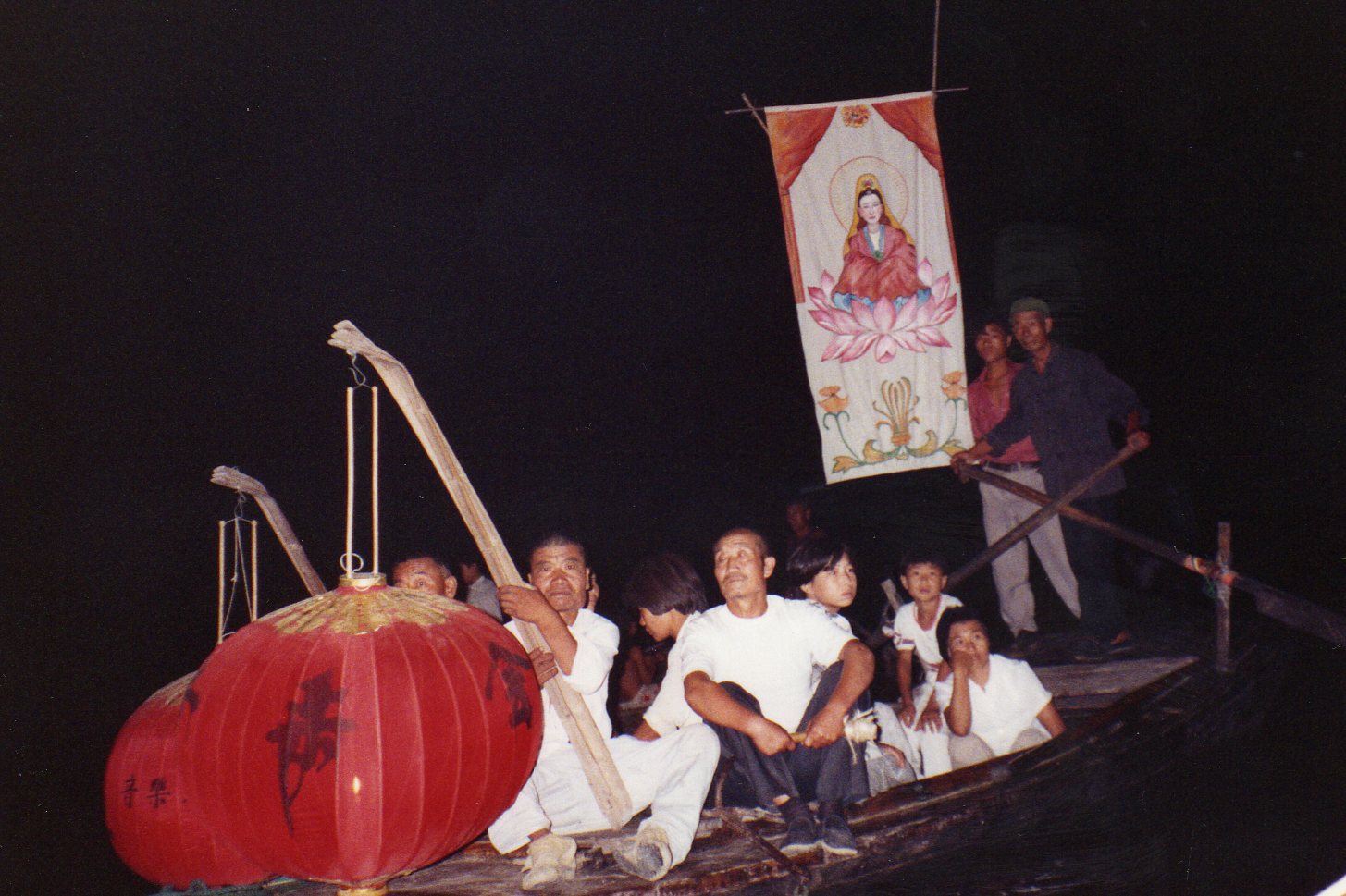
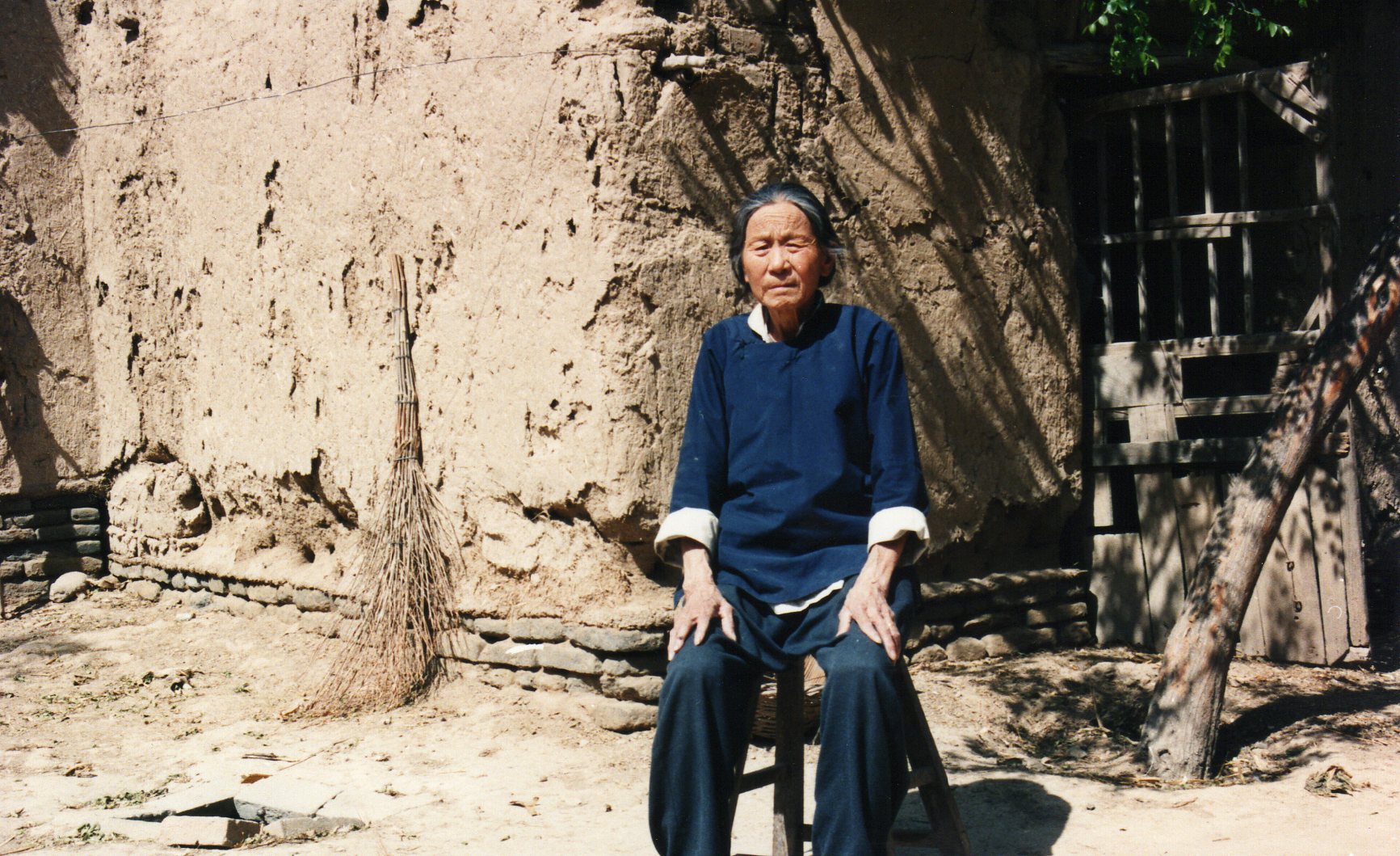
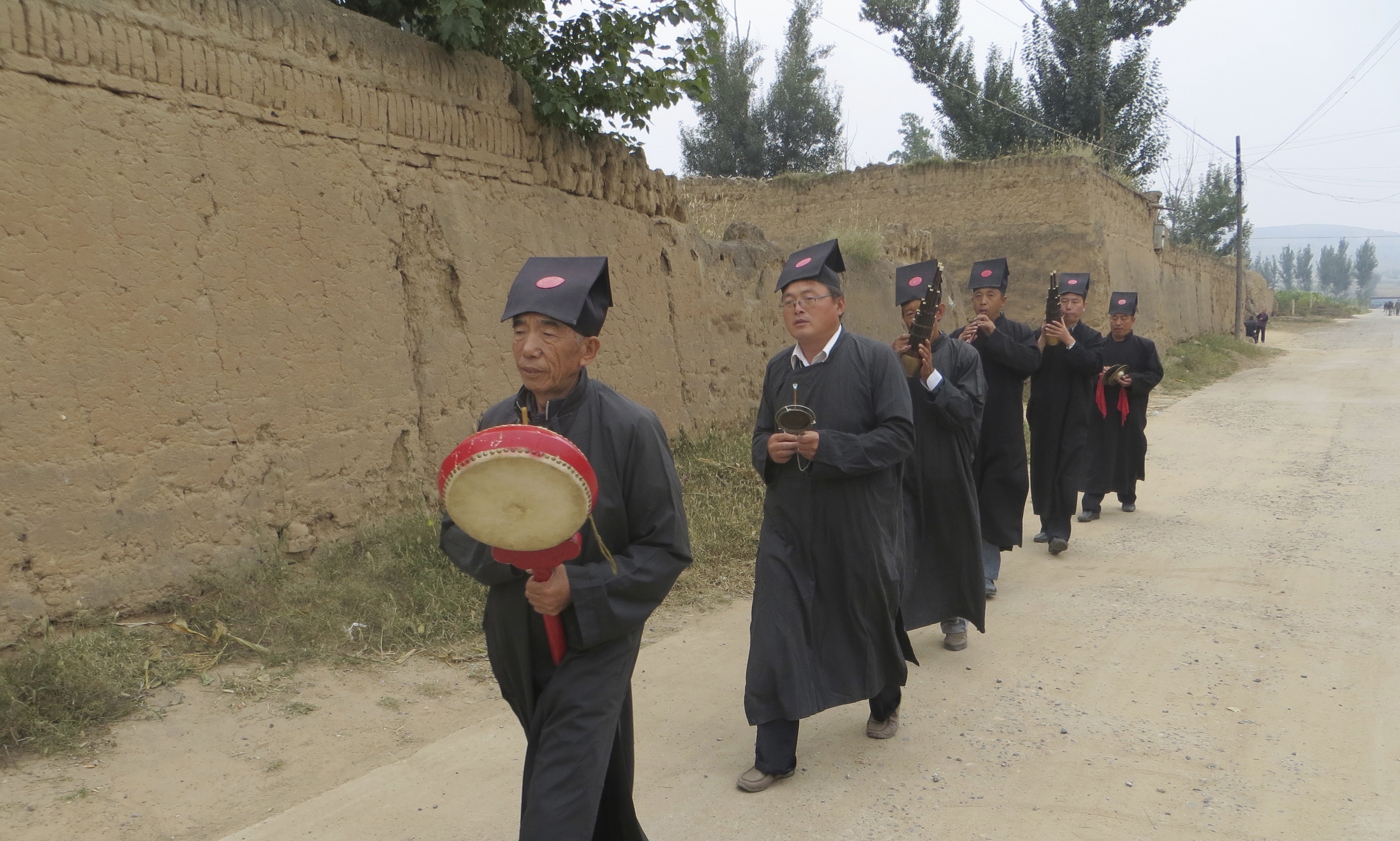
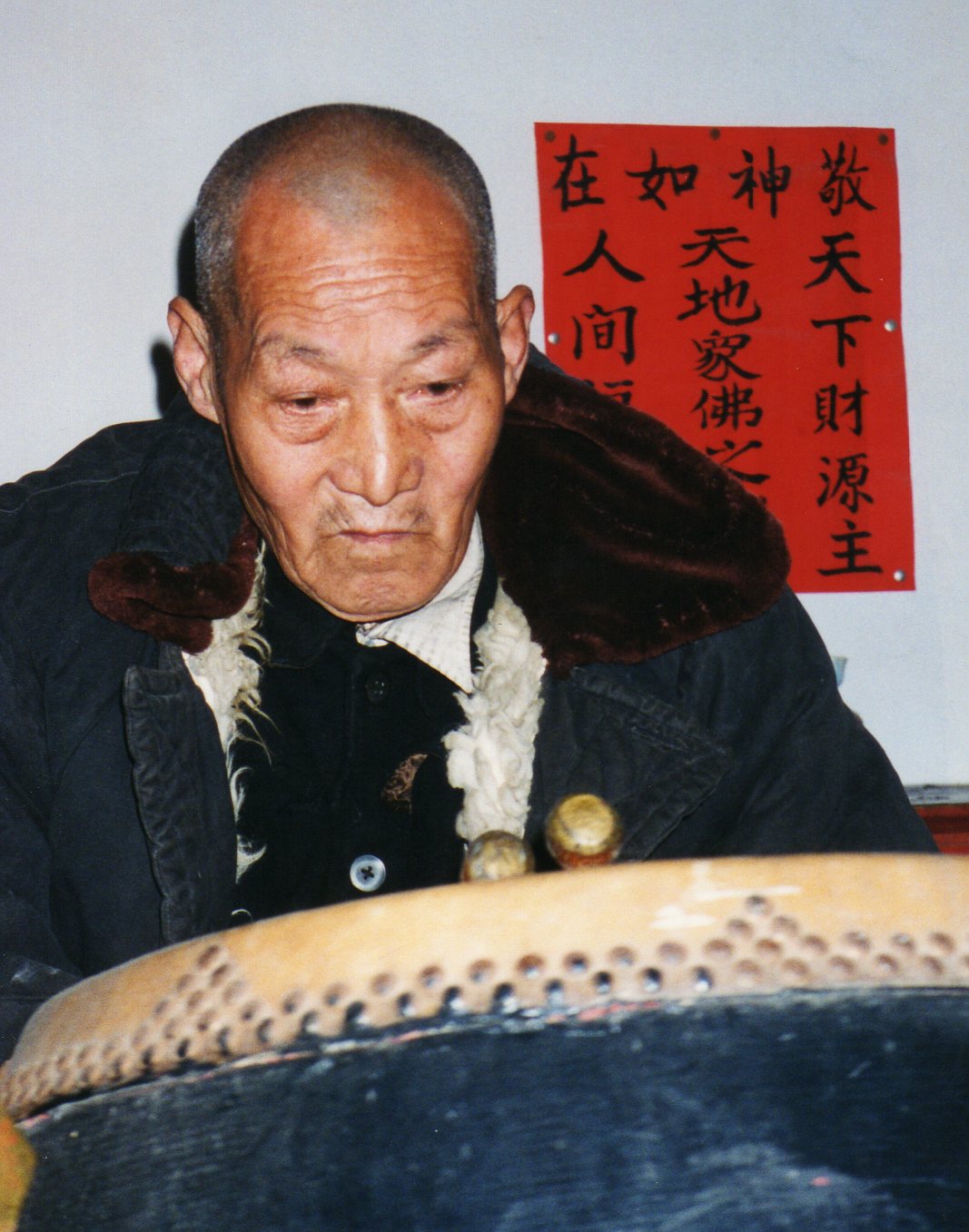
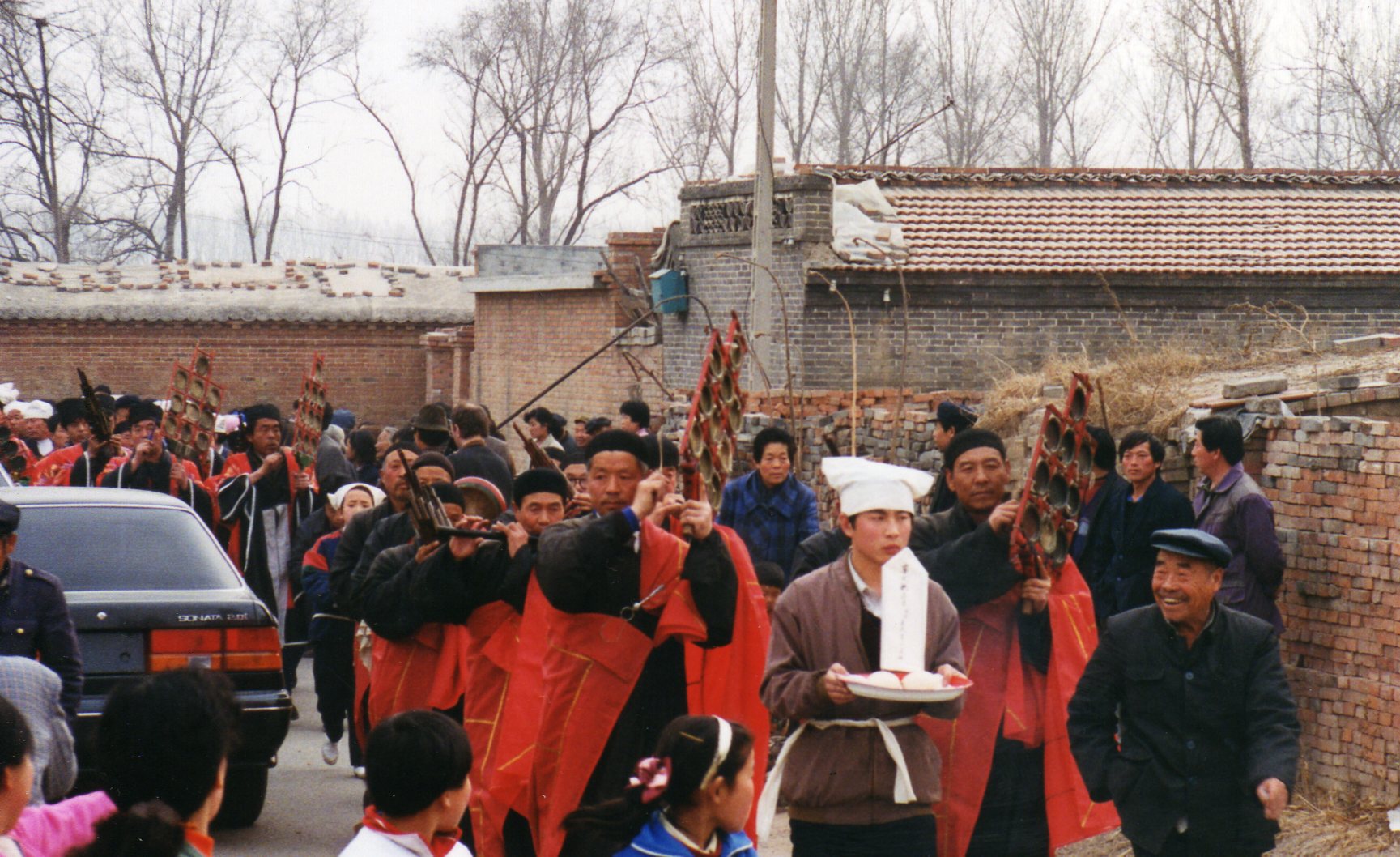
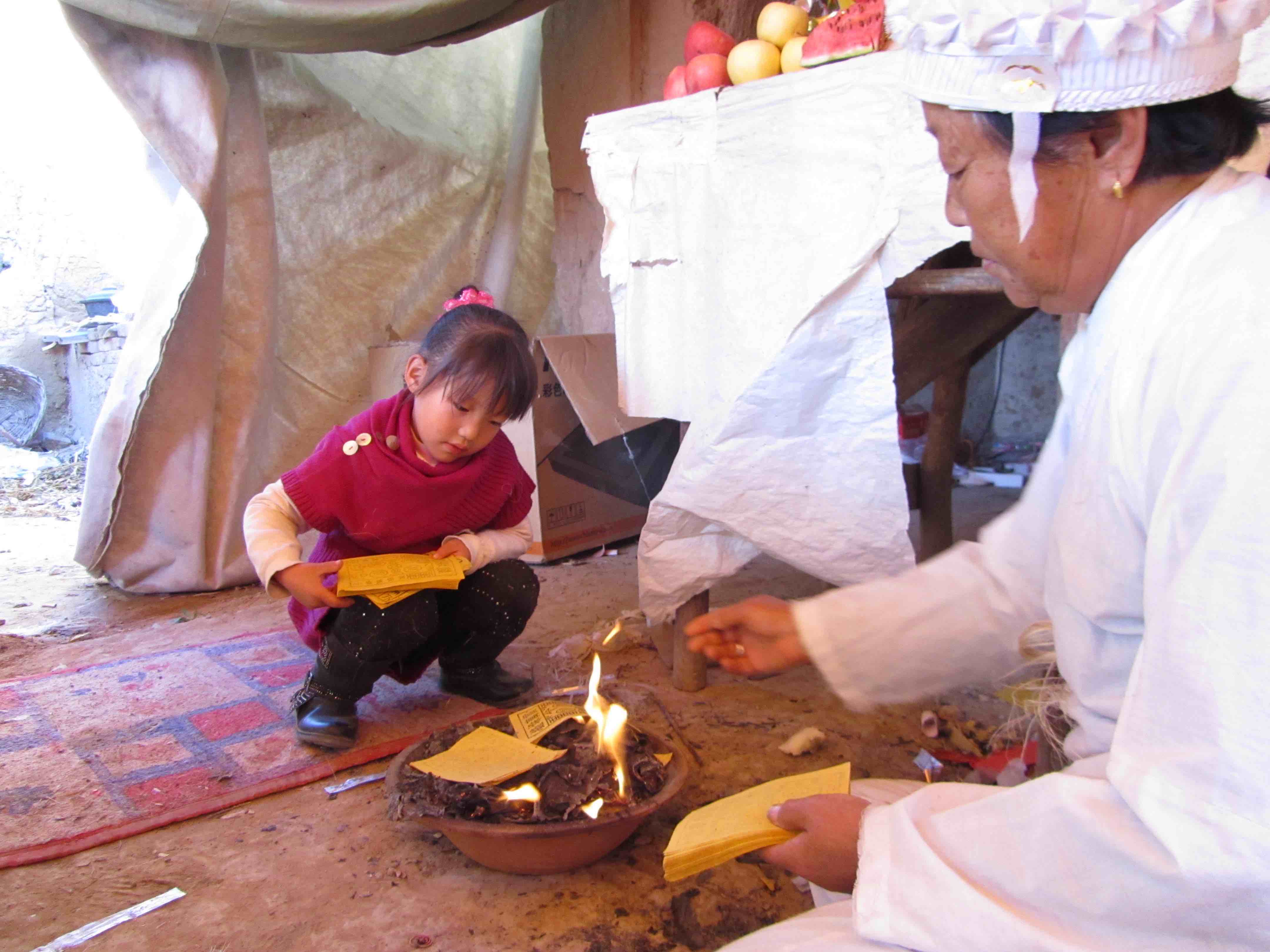





































 So while there are complex issues at work here, the recent directive illustrates a common befuddled knee-jerk response from local government. If they’re so keen on harking back to Maoist values, they might instead consider a re-education campaign for cadres—it is they who now lead the way in “vulgarity” and
So while there are complex issues at work here, the recent directive illustrates a common befuddled knee-jerk response from local government. If they’re so keen on harking back to Maoist values, they might instead consider a re-education campaign for cadres—it is they who now lead the way in “vulgarity” and 




 .
.









