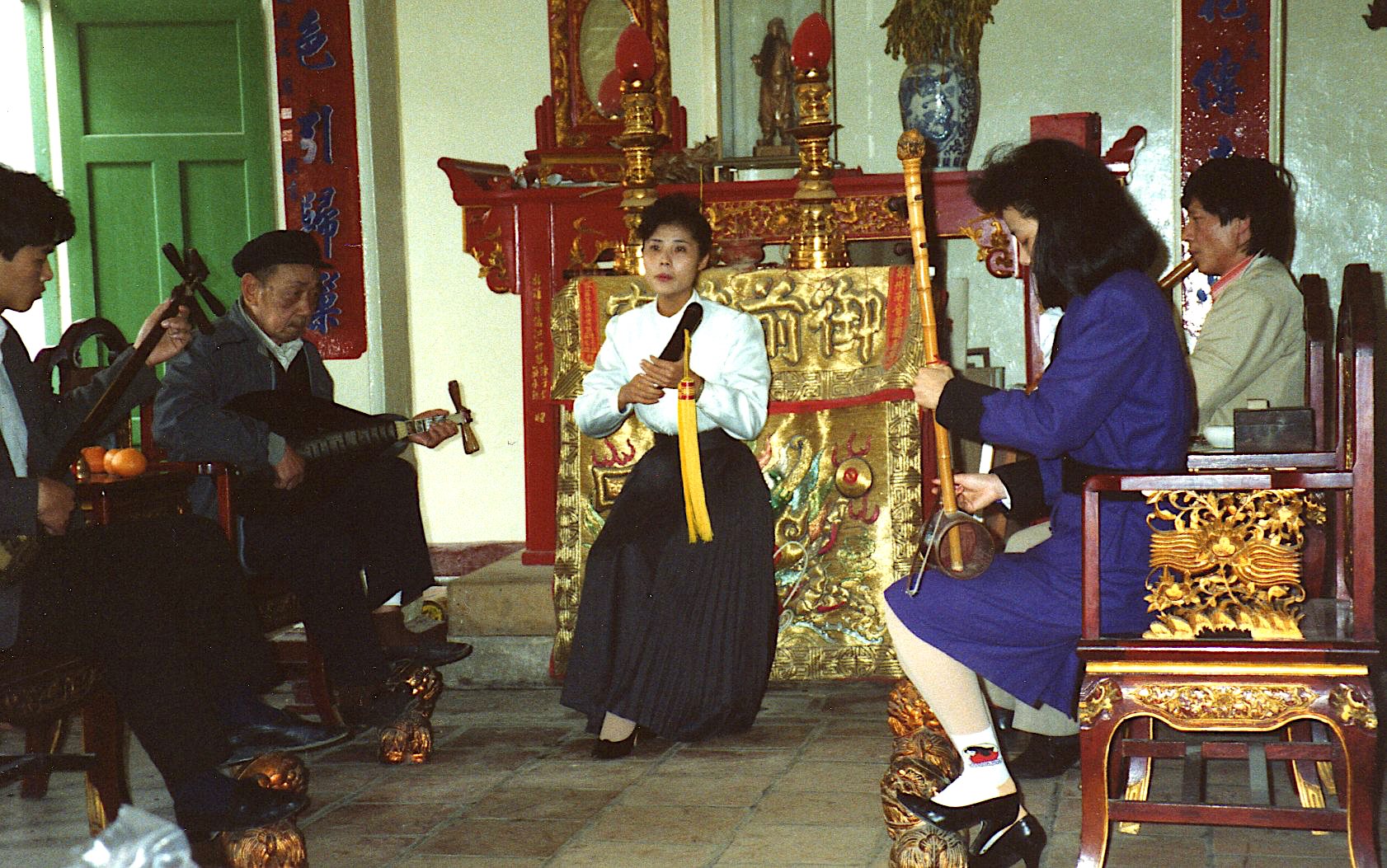
Qinglian street club, Old Westgate, Shanghai 2001. My photo.
The Jiangnan sizhu (“silk-and-bamboo of south Jiangsu”) instrumental ensemble has become a reified image of secular Chinese entertainment music. It’s played not only by polished professionals on stage, but by amateur groups in teahouses and leisure centres around Shanghai and the whole vicinity (for amateur chamber ensembles elsewhere, cf. suite-plucking in old Beijing, the Yulin “little pieces”, nanyin, and so on). Shanghai is a hospitable cosmopolitan urban centre, and these clubs are a popular haunt of foreign music students there.
The title was formalized only in the 1950s—one of many instances of the official renaming of genres at the time, such as Xi’an guyue or Xiansuo shisantao. Yet however one may dispute reification, Jiangnan sizhu is indeed “a thing”. Over a long period since the early 20th century we can observe a continuum from life-cycle and calendrical performances, through the amateur clubs, to professional staged performances.
In Chapter 13 of my book Folk music of China I began to put silk-and-bamboo in the wider context of musicking around south Jiangsu (Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, Changshu, Yangzhou, and so on—all large regions each containing several hundred villages!). And I outlined the background of regional opera, narrative-singing, and all kinds of ritual practice, including the Shifan ensembles that accompany Daoist ritual. Indeed, Daoist ritual around Shanghai and south Jiangsu is a vast topic subsidiary only to local traditions in southeast China.
So apart from their use as entertainment in the amateur clubs, the various types of sizhu have a firm basis in life-cycle and calendrical rituals.
Folk-singing in the region is easily overlooked, but fortunately we have a wonderful detailed study by Antoinet Schimmelpenninck, who also saw the wider picture. She refers to ritual styles like xuanjuan 宣卷 performed by devotional sectarian groups, common throughout south Jiangsu. [1]
As Chinese genres go, compared with many traditions in both north and south China Jiangnan sizhu is rather youthful. As commonly with folk groups, the musicians sit around a table, an inevitable casualty of stage performance. They often take turns on various instruments over the course of an afternoon session. The personnel remains predominantly male.
Chinese studies have favoured “music” over social context, and most publications on Jiangnan sizhu are based on the “eight great pieces” (for a simple introduction, see my Folk music of China, pp.275–82). While the repertoire is not so reified as this canonization may lead us to suppose, in the teahouses of central Shanghai it remains rather limited. But local variants of the repertoire abound, as shown by the definitive 1985 collection of transcriptions (770 pages!) by Gan Tao 甘涛. As always, we should regard it not as a reified repertoire, but as a regional form of musicking, a social activity (and since the ambience and sound-world of the amateur clubs may be reminiscent of Irish pub sessions, do enjoy my posts on Cieran Carson!).
See also this modest update.
Interlude: laowai
By the 1980s the Jiangnan sizhu repertoire was already the subject of analysis from scholars like Ye Dong, Li Minxiong, and Yuan Jingfang. Meanwhile, as China opened up again after the end of the Cultural Revolution, Larry Witzleben spent extended periods based at the Shanghai Conservatoire from 1981 to 1985, resulting in the brilliant early monograph
- J. Lawrence Witzleben, “Silk and bamboo” music in Shanghai: the Jiangnan sizhu instrumental ensemble tradition (1995),
still one of the most accomplished ethnographies of a local Chinese tradition.
With chapters on the historical background and intergenre relationships, instruments, repertory, form, variation, texture, and aesthetics, perhaps the most innovative section is Chapter 2, a nuanced ethnography of the scene from 1981 to 1985, including relations with the professional music world.
Silk-and-bamboo soon earned a significant place in Western scholarship, and images of Chinese music, also thanks to the writings of Alan Thrasher, albeit concerned more with musical structures than with ethnography.
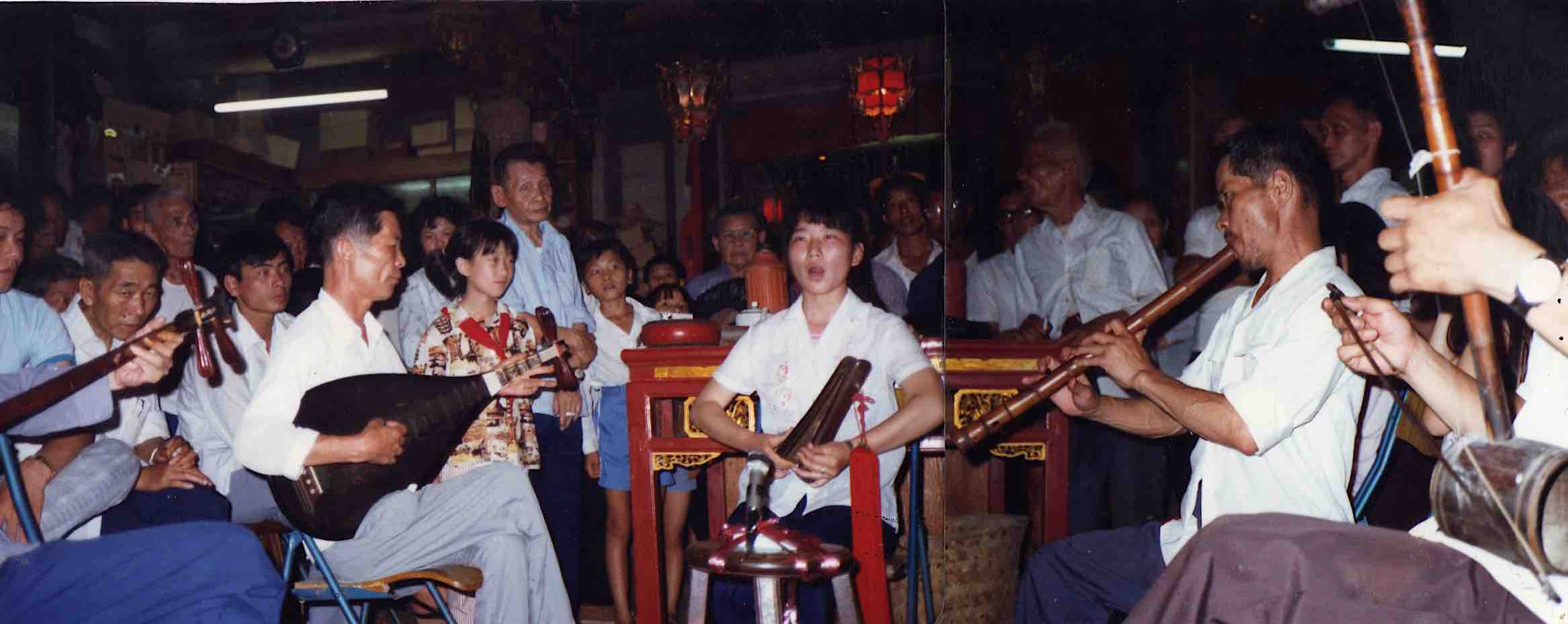
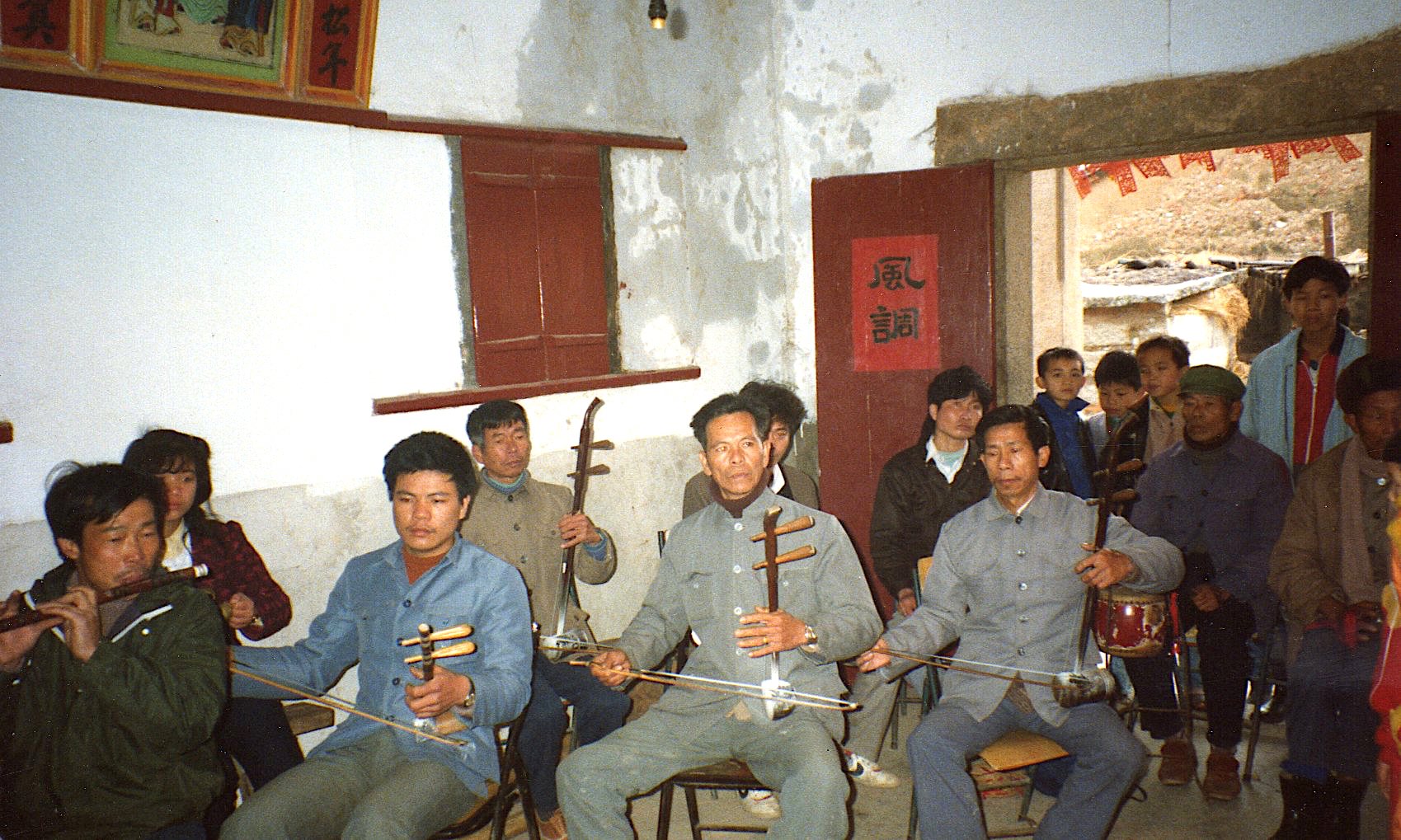
Silk-and-bamboo clubs, Shanghai 1987. My photos.
In 1986 and 1987, based in Beijing, I used to decamp to Shanghai occasionally, taking what was then a very long train ride. According to my own apocryphal story, my main incentive was that the showers of the foreign students’ dorms there had a rather reliable supply of hot water, still rare in my student accommodation in Beijing. Anyway, even though I was already entranced by northern ritual culture, it gave me an opportunity to take part in some of the many amateur silk-and-bamboo clubs on erhu fiddle—and also to hang out with the wonderful qin-player Lin Youren and acquaint myself with the thriving Daoist ritual scene.
For foreign students, participant observation was both instructive and pleasurable. As laowai, we were more keen on visiting the teahouses than our Chinese fellow-students, who naturally focused on the polished versions of their conservatoire teachers.
In 1987 I was roped into a Jiangnan sizhu contest at the conservatoire, joining a mixed group of Chinese and foreign students—the latter including François Picard, Fred Lau, and Tony Wheeler (back row, to my right). In the front row, on the far right is Ma Xiaohui 马晓晖, who went on to a career as erhu virtuoso, and at the centre is Zhou Zhongkang 周仲康, the conservatoire teacher assigned to oversee our efforts—our programme included his luogu sizhu composition Qing 庆:

The competitive format was hardly my favoured method of engaging with silk-and-bamboo, but it was an interesting experience. Alongside the conservatoire-style ensembles taking part, there were also some fine senior amateur groups. As cute foreign pets we inevitably won a prize, but our sound ideal, however flawed in execution, was modelled on folk practice rather than the more polished version of the professionals. Soon after, Helen Rees also became a regular participant at Shanghai teahouse sessions, while embarking on her fine studies of ritual music in southwest China.
Thinking back, guided by mentors at the Music Research Institute and Yuan Jingfang, my Beijing base propelled me towards ritual in the countryside more inevitably than might have been the case if I had been studying in Shanghai. Rural ritual is plentiful throughout south Jiangsu too, but somehow there is more to encourage one to tarry in cosmopolitan Shanghai without venturing out to the villages and townships.
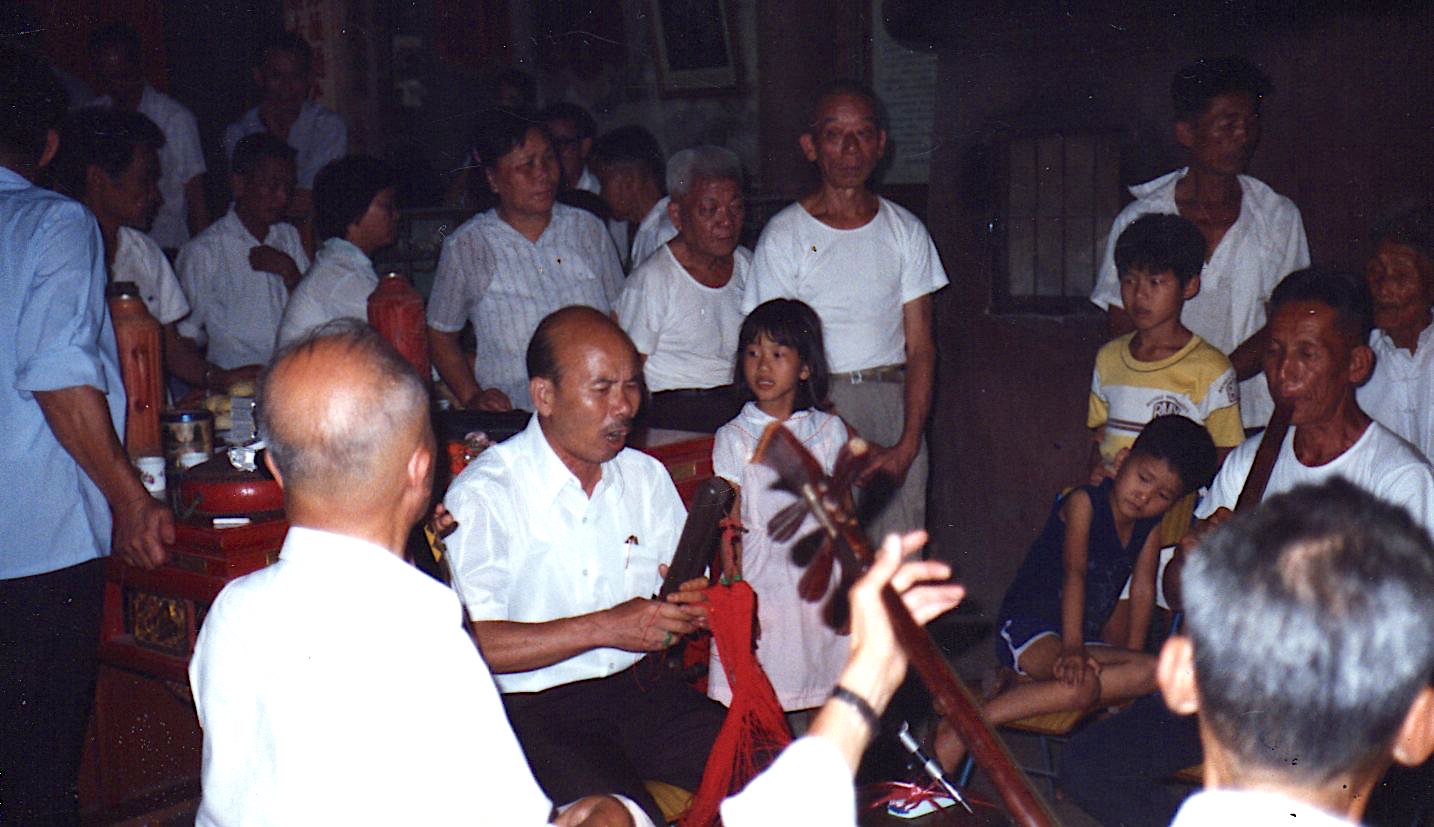
Zhang Zhengming, 2001: left, with Zhou Hao at the Xuhui club;
right, with his wife—their 1952 wedding photo in the background.
On a visit in 2001 I spent a week in Shanghai, with the wonderful Zhang Zhengming 张徵明 (b.1925) guiding me to a different club every afternoon. It was good to see the renowned erhu master Zhou Hao, then 77, taking part keenly in the amateur groups, naturally modifying his polished style to the ambience; later in a one-to-one session he gave me a fine demonstration of the difference between “folk” and “conservatoire” styles.

I was happy to be able to invite a group led by Zhang Zhengming to the 2005 Amsterdam China festival, as I scurried around hosting the Hua family shawm band and the Li family Daoists from Yanggao.
Again, there’s a continuum: official staged presentations are part of the whole fabric of silk-and-bamboo. This playlist from Jan Chmelarčík includes his videos from the amateur clubs in 2006 and 2007, showing a variety of contexts and styles:
The silk-and-bamboo scene plays a major role in Ruard Absaroka’s thesis Hidden musicians and public musicking in Shanghai, very much informed by anthropological theory. [2]
The wider context: the Anthology
It’s so easy to find activity in central Shanghai that one might not be tempted to explore the suburbs and further afield. But by the 1980s, research was also expanding significantly with the great Anthology:
- Zhongguo minzu minjian qiyuequ, Shanghai juan 中国民族民间器乐曲, 上海卷 (1993),
edited by the knowledgeable Li Minxiong.
Local collectors documented the wider region in the suburbs of Shanghai, with its twelve municipalities and ten counties. Apart from transcriptions, the collectors also described folk activity, with useful textual introductions as well as biographies and introductions to major groups.
Again it’s worth noting the overall Anthology coverage for Shanghai. After an opening section on solo music (pp.19–234) devoted mainly to pipa solos, there are three main rubrics: sizhu (235–930), chuida (932–1268), and “religious music” (1273–1594). There follow brief biographies and accounts of folk groups (1595–1638, illustrated descriptions of instruments (1639–58), and lengthy appendices, mainly gongche scores (1661–2087).
It may seem impressive that even by 2001 over thirty sizhu groups were still meeting amidst the glossy modernity of central Shanghai. But for the whole region, Li Minxiong gives a figure of 428 groups (!) since the early 20th century; as he explains in his introduction (JC pp.241–63), over two hundred were active on the eve of Liberation.
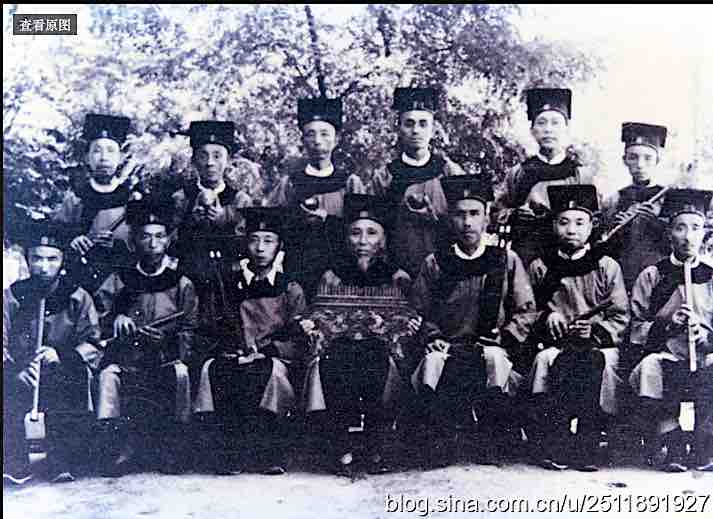
Following the May Fourth movement of 1919, many groups adopted the term “national music” in their titles. Indeed, such groups were the precursors of the whole “conservatoire style” that later came to represent the official image of Chinese music. The Anthology describes celebrated groups from the Republican era.

Top: Xiadiao music ensemble; middle: Qingping gathering, 1934; below: Datong music association (note music stands!). Source: Zhongguo minzu minjian qiyuequ jicheng, Shanghai juan.
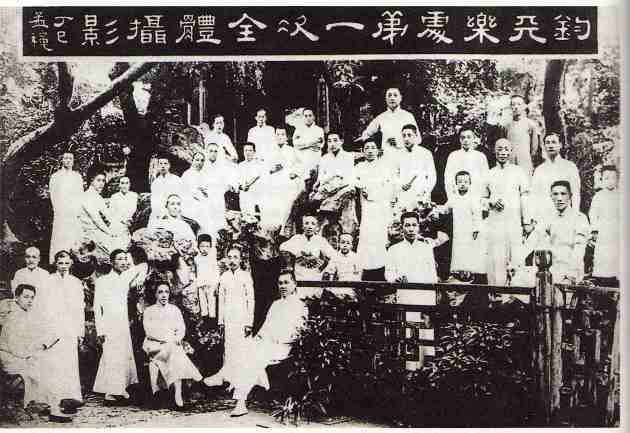
Juntian gathering, 1917, Source: Qi Kun, Jiangnan sizhu.
After the 1949 Liberation, master musicians from the “old society” lent continuity, such as Jin Zuli, Sun Yude, Li Tingsong, Wei Zhongle, Chen Yonglu, and Lin Shicheng (for more, see Anthology, pp.1595–1722). At the same time they were responsible for certain innovations resulting from adapting the style to the concert platform. Commercial recordings were already quite common, but the carefully prescribed arrangements of Lu Chunling’s quartet with Ma Shenglong, Zhou Hao, and Zhou Hui became influential. Here’s a cassette (remember them?) of them from 1982, after the hiatus of the Cultural Revolution:

As collectivization and campaigns escalated, some folk groups had difficulty maintaining activity; but, as everywhere, the liberalizations following the collapse of the commune system in the late 1970s brought a revival. In 1980 over seven hundred performers took part in a grand performance at the Shanghai conservatoire, with groups coming from Shanghai, Suzhou, Wuxi, Nanjing, and Hangzhou. But as Shanghai was transformed again, amateur clubs have somehow remained active.
Related genres
But apart from the public image of sizhu, the Anthology valuably introduces bands in the surrounding suburban regions, often serving life-cycle and calendrical rituals—in Nanhui, Fengxian, Chuansha, Jiading, Shanghai county, Baoshan, Qingpu, Songjiang, Jinshan, and Chongming island.

Undated Anthology photos: above and below: chuida bands, Chongming; middle: the Tianshan national music association.
So this involves expanding our explorations in terms of both geography and genre. While sizhu is the main theme, the plot thickens when we include related instrumental genres hardly broached by foreign scholars based in metropolitan Shanghai: the “pure tones bands” (qingyin ban 清音班) and the former tangming 堂名 groups (see also n.3 below).
Moreover, the latter are also related to the occupational “blowing and beating” bands (chuidaban 吹打班) based on shawms and percussion—another main rubric of the Anthology (see introduction, pp.932–45). Among 184 such bands for which collectors found evidence, Li Minxiong gives sketches of rural groups in Chuansha, Baoshan, Qingpu, and Jiading, all with several generations of transmission. This section also contains material on local ritual, including weddings, funerals, and longevity celebrations (qingshou 庆寿), as well as calendrical and religious rituals.
A fine case-study: Nanhui
Qi Kun 齐琨, with a firm background in music anthropology, has produced some fine ethnographic work, notably her book on the qingyin 清音 groups of Nanhui county in the southeastern suburbs [2]—itself an extensive area, with 26 districts (amalgamated in 2001 into 14 townships) and 347 villages:
- Lishidi chanshi: Shanghai Nanhui sizhuyue qingyinde chuancheng yu bianqian yanjiu 历史地阐释: 上海南汇丝竹乐清音的传承与变迁研究 (2007).
Starting from around 1850 when such groups became common in Nanhui, she uses local gazetteers, interviews with senior performers, and fieldnotes from attendance at rituals and secular performances. She often cites the Nanhui draft for the Anthology, which looks to be among the more detailed local contributions to the Shanghai volumes.
She introduces various related genres in Nanhui, including Daoist groups [3] and their former “household kin” (menjuan 门眷) catchment-area system, occupational chuida bands, Buddhist groups, opera, and the Pudong style of pipa plucked lute.
Qi Kun musters impressive material on bands and activity in the late Qing and the Republican era (itself a period of significant change), with sections on temple fairs, weddings, and funerals.
After the Communist victory of 1949, state-sanctioned performances of Jiangnan sizhu on stage became more common alongside traditional contexts, but as always I’m keen to learn more about folk activity during the decades of Maoism, the crucial transitional period from the “old society” to the consumer culture of the reform era (cf. Yulin).
The Anthology notes in passing some basic elements in the decline of many groups over the period as a result of the state’s pervasive social remoulding, such as migration, army service, collectivization, and campaigns against superstition. But ever alert to change, Qi Kun has a detailed chapter on the Maoist era in Nanhui. She illustrates the severe reduction of the diverse local social contexts that were the basis for expressive culture before Liberation—the rich network of temple fairs, weddings and funerals. Many qingyin performers were absorbed into a scene now based on entertainment rather than ceremonial; as elsewhere, many fine folk musicians were recruited to the new state-funded opera troupes and amateur “art-work troupes”. Qi Kun notes the place of qingyin in state-sponsored events like political meetings and sending off army recruits.
However, there was a certain continuity, and amateur qingyin activity persisted. Qi Kun gives instances from nine districts. She notes the more-or-less undisturbed observance of life-cycle rituals in the early 1950s, with lengthy processions; some groups even persisted performing for these contexts into the early 1960s.
The fortunes of musicians depended largely on their “class status”, but irrespective of this many were reduced to poverty. But there were ironies—as one performer commented:
People like Wen Zhengxiu who served as Daoist priests weren’t persecuted. Almost all of those Daoists smoked opium, so they had virtually no possessions at home, they could never become wealthy. So after Liberation they were classed as poor peasants. Instead it was honest people like us, who had toiled over several generations to accumulate family property, who were targets of punishment.
Such people now became the core of many qingyin groups.
Amidst the traumas of the Cultural Revolution, Qi Kun goes on to describe the maintenance of the qingyin style (if not its former context) in the Mao Zedong Thought propaganda troupes. Some troupes even used the traditional sizhu repertoire, like Xingjie, to accompany political processions.
And even now a certain amount of furtive recreational activity continued (again, cf. Yulin)—behind closed doors, some troupe members even sometimes dared invite former “landlords” and “rich peasants” to play the traditional repertoire along with them. Performers recall both the cruelty and the nuances of the period. Many of the troupe members became core elements in the revival of tradition from the late 1970s—for which, of course, the main factor was the amazing resurgence of ritual practice. Indeed, a modest revival was already under way before the overthrow of the Gang of Four in 1976.

Qingyin bands in Fengxian, Jiading, and Baoshan. Source: Anthology.
In Chapter 4 Qi Kun takes the story on into the consumer age. After detailing the gradual revival (cf. my own notes on that of the Li family Daoists in Shanxi), she surveys a scene that is still more diverse than that before 1949, with recreational groups (now under semi-official leadership, with some even adopting the title “folk music band” minyuedui 民乐队!) now able to meet regularly, overlapping with occupational bands performing for customary observances. She gives a fine diary of the varied public activities of the Zhuqiao qingyin band from 1994 to 2003, as well as detailed notes on a 2002 wedding and on the grandest of ten funerals that she attended in 2004. Indeed, while such groups traditionally performed for weddings, their participation in funerals is a recent innovation.

Still, even with the revival, fewer performers are active than before 1949. Qi Kun also illustrates changes in ritual practice over the period with graphic tables. Here she compares figures for qingyin bands active around Nanhui in 1937–49 and in 2004, by district:

For all periods, Qi Kun constantly notes the interaction of social, economic, political, and musical change—if only Chinese musicology would learn from such an approach, rather than banging on about heritage and living fossils!

Wall advertisement for the Tongxin qingyin band, Nanhui c2004. Source: Qi Kun, Jiangnan sizhu (2009).
The advertisement above reads:
Exclusive service for wedding and funerals: destroy superstition and be frugal—stylish and trendy.
I don’t know if this was a disingenuous response to a temporary campaign, but the social mood of the time was not exactly keen on destroying superstition or enacting frugality. Discuss…
And suburban regions like Nanhui are anything but a rural backwater: they are inextricably tied to the global economic market of Shanghai. But exploring the environs always reveals a diverse picture.
That’s quite enough for one sitting—but zooming out still further, the instrumental volumes of the Anthology for Jiangsu province give an impression of such bands throughout the province:
- Zhongguo minzu minjian qiyuequ, Jiangsu juan 中国民族民间器乐曲, 江苏卷 (1998).
Again its main rubrics are chuida, sizhu, and “religious music”.
And just south lies Zhejiang province… Aiyaa.
* * *
Shanghai silk-and-bamboo makes a comfortable repertoire that is too easily reified and detached from the wider society. Much as I have enjoyed visiting the Shanghai teahouses, there’s so much more to study, not only in the suburbs but all around south Jiangsu, where entertainment genres are always subsidiary to ritual! And the cast of ritual performers, here as elsewhere, is still more varied: Daoist ritual specialists, spirit mediums (very important in local society), devotional sectarian groups, and so on.
Like Beijing, Tianjin, Chongqing, and other municipalities, Shanghai is a vast region, the riches of whose expressive culture can hardly be encapsulated by simple labels. As usual, we have to look beyond the reified canons of idealized, “representative” “genres” (the Zhihua temple, the “eight great suites” of Shanxi, the Uyghur twelve muqam, and so on) and plunge into the complex world of changing local social activities.
[1] Among considerable research on xuanjuan, see e.g. articles in Dayin 大音 vols. 3, 4 and 5; Zhongguo quyi zhi, Jiangsu juan 中国曲艺志, 江苏卷; Qian Tiemin 钱铁民 (on Wuxi) in Zhongguo minjian yishi yinyue yanjiu, Huadong juan 中国民间仪式音乐研究, 华东卷 (2007) vol.1; Qiu Huiying 丘慧瑩, “Jiangsu Changshu Baimao diqu xuanjuan huodong diaocha baogao” 江蘇常熟白茆地區宣卷活動調查報告, Minsu quyi 169 (2010), pp.183–247; Li Shu-ju 李淑如, “Zhangjiagang diqu jianwang fahui yishi yu xuanjuan diaocha baogao” 張家港地區薦亡法會儀式與宣卷調查報告, Minsu quyi 204 (2019.6), pp.197–250. In English, see Mark Bender, “A description of ‘jiangjing’ (telling scriptures) services in Jingjiang, China”, Asian folklore studies 60 (2001), and ongoing work from Rostislav Berezkin, such as this, and an article with Vincent Goossaert.
[2] For a flavour [sic] of his recent musings, see “Timbre, taste and epistemic tasks: a cross-cultural perspective on atmosphere and vagueness”, in Friedlind Riedel and Juha Torvinen (eds), Music as atmosphere: collective feelings and affective sounds (2019), which sets forth from timbre and atmosphere in Shanghai silk-and-bamboo. While I like the title, and am happy to add the splendid acronym WEIRD (coined to describe “western, educated, industrialized, rich, and democratic” ethnocentrism) to my list, I may not be alone in finding some of his erudite theoretical discussion a tad arcane. That’s academia for you!
[3] Qi Kun also has related articles in Zhongguo minjian yishi yinyue yanjiu, Huadong juan (with film footage on the DVD), and the Dayin series (n.1 above).
[4] For Daoist ritual in Nanhui, see Zhu Jianming 朱建明 and Tan Jingde 谈敬德, Shanghai Nanhui xian Zhengyi pai daotan yu Dongyue miao keyiben huibian 上海南汇县正一派道坛与东岳庙科仪本汇编 (2006), and Zhu Jianming and Tan Jingde, Shanghai Nanhui xian Laogang xiang nongjia duqiao yishi yu qiao wenhua 上海南汇县老港乡农家渡桥仪式与桥文化 (1996); in Jiading and Chuansha counties, Zhu Jianming, Tan Jingde, and Chen Zhengsheng 陈正生, Shanghai jiaoqu daojiao jiqi yinyue yanjiu 上海郊区道教及其音乐研究 (2001; for the tangming groups, note pp.29–48); and in Shanghai county, Zhu Jianming, Shanghai xian Shengtang daoyuan jiqi taiping gongjiao kaocha jishi 上海县圣堂道院及其公醮考察纪实 (1993). See also a thoughtful review by Poul Andersen in Daniel Overmyer, Ethnography in China today, pp.263–83.










 To accompany my new post outlining diverse performance genres of
To accompany my new post outlining diverse performance genres of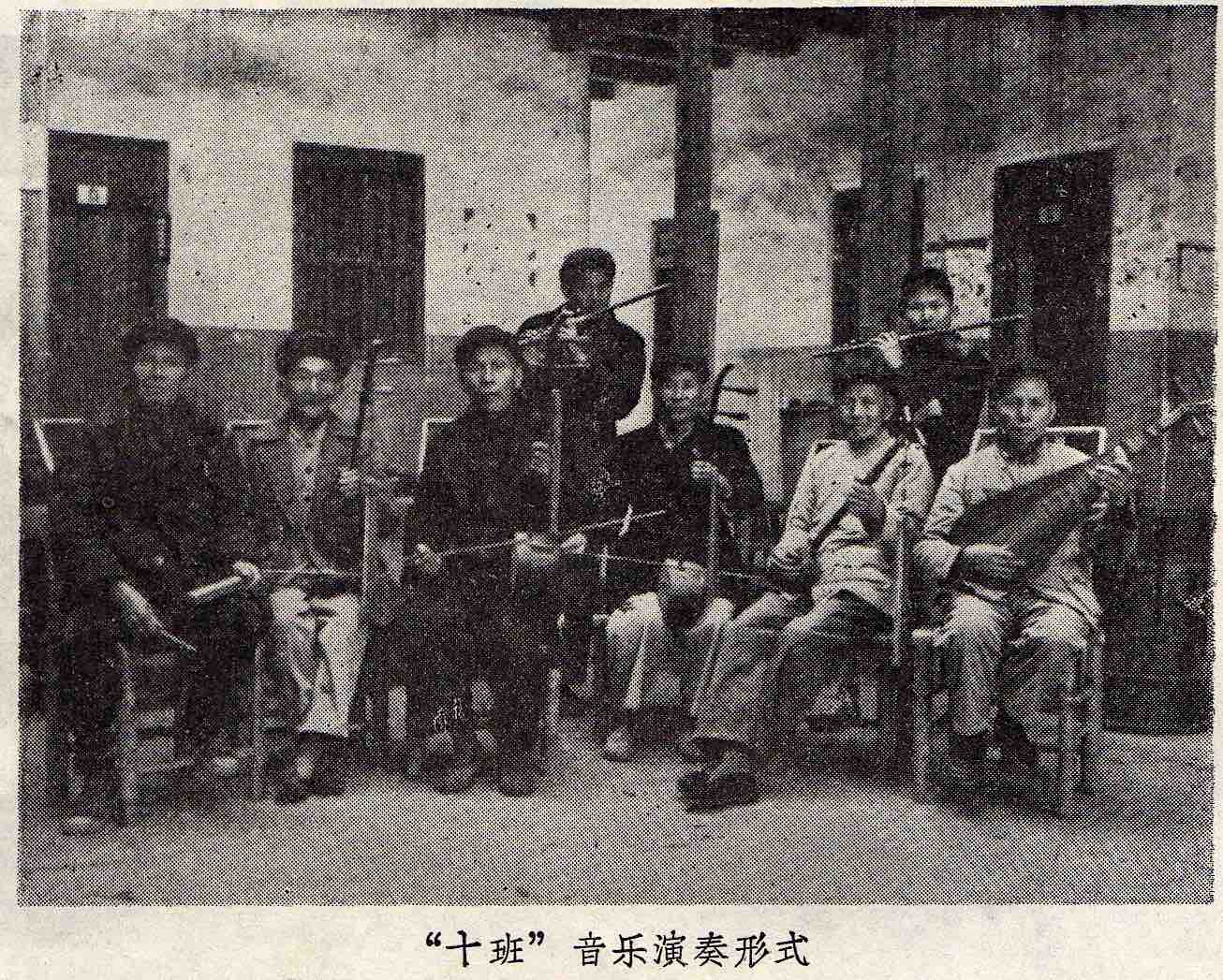 




















































 What did persist in Beijing, both before and since the Cultural Revolution, was the amateur narrative-singing scene—a must for any aficionados of
What did persist in Beijing, both before and since the Cultural Revolution, was the amateur narrative-singing scene—a must for any aficionados of 
























 Still, even photos of ritual practice remain silent and immobile. Given that ritual is
Still, even photos of ritual practice remain silent and immobile. Given that ritual is 








 So while there are complex issues at work here, the recent directive illustrates a common befuddled knee-jerk response from local government. If they’re so keen on harking back to Maoist values, they might instead consider a re-education campaign for cadres—it is they who now lead the way in “vulgarity” and
So while there are complex issues at work here, the recent directive illustrates a common befuddled knee-jerk response from local government. If they’re so keen on harking back to Maoist values, they might instead consider a re-education campaign for cadres—it is they who now lead the way in “vulgarity” and 


 Along with regions like
Along with regions like 
 In Wuxi, under the tuition of the American missionary
In Wuxi, under the tuition of the American missionary 







