North Shanxi Arts Work Troupe, Datong 1959. Li Qing front row, far right.
My post on the folk–conservatoire gulf reminds me of the brief sojourn of the great household Daoist Li Qing in the grimy coal city of Datong as a state-employed musician. Indeed throughout China, many “folk artists” were recruited to such troupes, like wind players Hu Tianquan and Wang Tiechui. Daoists were also enlisted (see e.g. Ritual life around Suzhou, §5); Daoist priest Yang Yuanheng even served as professor at the Central Conservatoire in Beijing until his death in 1959.
But under Maoism the “food-bowl” of the state troupes was short-lived; most employees were soon laid off. And while in the troupes, performers’ lives were no picnic: the whole society was poor, all the more so during the Years of Hardship while Li Qing was employed.
The following is adapted from ch.5 of my Daoist priests of the Li family.
In the early years after the 1949 Liberation, religious ritual in Yanggao had persisted despite sporadic campaigns and the nominally atheist stance of the new Communist leadership. But by 1954, as collectivization began to be enforced ever more rigidly (see here, under “Famine in China”), creating ever-larger units which made it hard to protect local interests, and with ambitious new mobilizations taking up more and more time, it was becoming increasingly hard to “do religion.” The main thrust of campaigns may have been economic, as household enterprises were forced into inactivity; but “eliminating superstition” was never forgotten, and was to be one explicit slogan of the 1958 Great Leap Forward.
Li Qing eats off the state
When not busy laboring in the collective fields or doing rituals, Li Qing enjoyed playing his beloved sheng mouth-organ in the village’s amateur “little opera band”, accompanying both the majestic “great opera” (Jinju) and the skittish local errentai duets. In the bitter cold of the first moon in 1958 Li Qing, now aged 33 sui, made the journey to Yanggao county-town to take part with his village band in a secular arts festival there. The county cultural authorities were choosing musicians for their Shanxi opera troupe, [1] and were keen to recruit Li Qing. But scouts attending from the prestigious North Shanxi Arts Work Troupe in the grimy regional capital city of Datong pulled more weight, and it was for this ensemble that he was now chosen. In this period regional arts-work troupes and county opera troupes throughout China commonly recruited Daoists and other folk ritual performers as instrumentalists (see e.g. under Ritual life in Suzhou). Li Qing was to spend nearly four years in the troupe. Thus, although they made regular tours of the countryside, he was protected somewhat from the worst excesses of the Great Leap Forward back home.
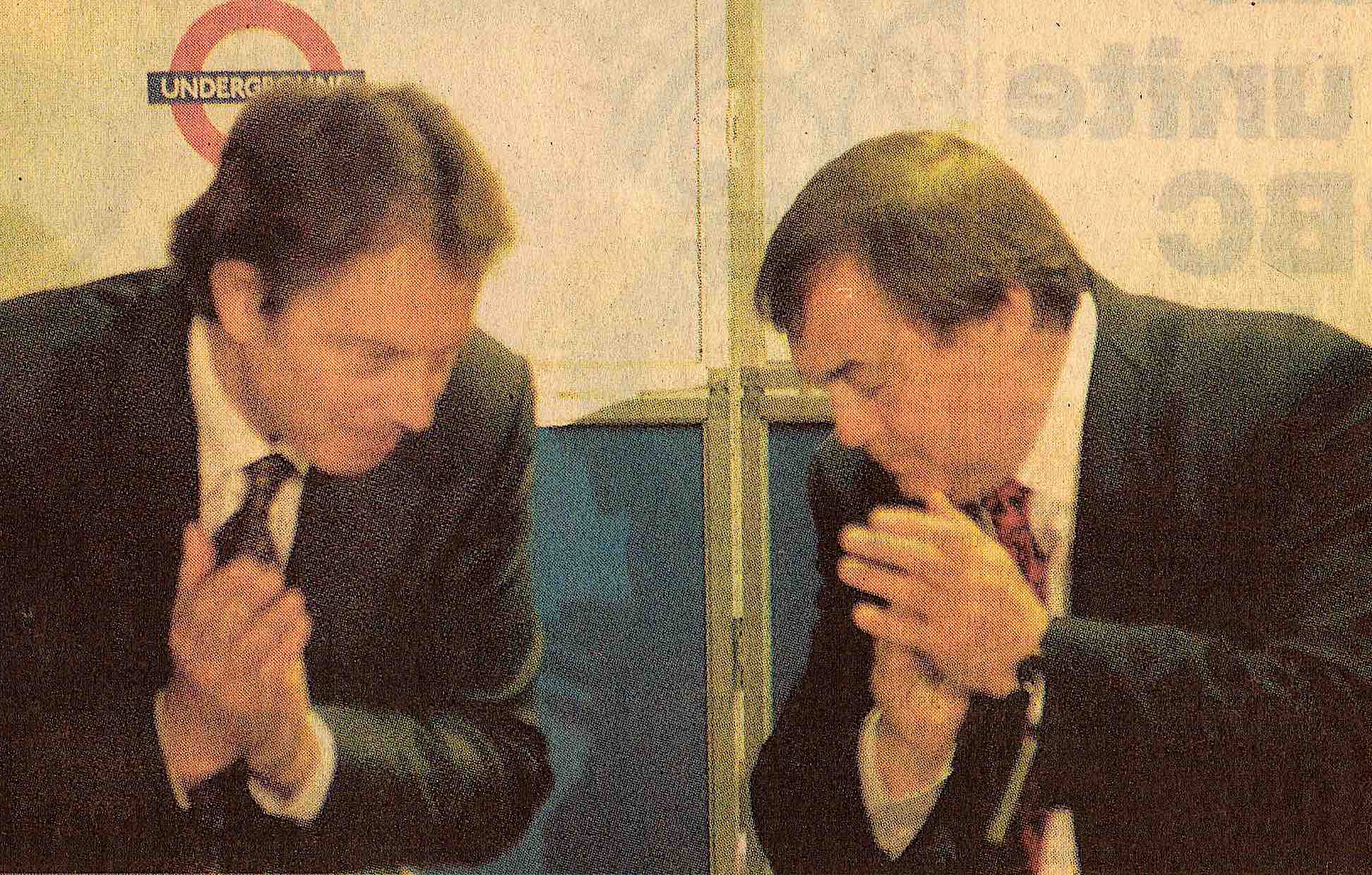
In 2011, to learn more about Li Qing’s time in the troupe I visited Datong to seek out some of his former colleagues there—Li Manshan and Li Bin had already bumped into a couple of them on trips there.
It’s good to see my old friend Bureau Chief Li again. We track down two old musicians from the troupe and invite them round to his posh flat where I am staying the night. It would make a tranquil venue, but since it is the time of the Mid-Autumn festival, an auspicious time for weddings, our chat is regularly punctuated by deafening firecrackers echoing around the high-rises, so that the soundtrack evokes the battle of the Somme.

Li Kui (left) and Zhang Futian, Datong 2011.
Li Kui, who played erhu fiddle in the troupe, and the effervescent Zhang Futian, a dizi flute player, both born in 1939, were 19 sui when they joined, thirteen years younger than Li Qing. Wary of hagiography as I am, all those who met Li Qing remain moved by his kindly soul and unsurpassed musicianship. Those years were not just a contrast to the rest of his life but a unique period for everyone. Recruitment to a prestigious state ensemble may sound grand—until you realize not only the desperate conditions of the late 1950s but that they spent much of the year touring the ravaged countryside on foot. Still, for them the period has a bitter-sweet nostalgia that I can’t help sharing. My visit provides an excuse for them to get together to reminisce about old times—they are so loquacious that I rarely get to chip in with a question.
Li Qing went off to Datong to take up his new job in the 8th moon of 1958, just as the Great Leap Forward was being rolled out to great fanfare. Even if he had a choice about taking the job, he can have had little hesitation. With Daoist ritual business, and society as a whole, going through such a tough period since the enforcement of collectivization, he would have been grateful to get on the state payroll.
The Party officials of the troupe must have found out about Li Qing’s rich-peasant status but drawn a veil over it. Throughout the Maoist period, the Yanggao cultural cadres didn’t dare have any contact with the Daoists or even the shawm bands—but the Datong troupe leaders didn’t need to know that Li Qing was a Daoist. His colleagues would find out, but everyone understood there was no need to discuss that kind of thing. He didn’t talk much at first, but became more chatty as he felt more at ease. For his closest friends he even furtively held sessions to determine the date.
The new troupe, based in a compound at no.13 Zhengdian street, was an amalgamation of the North Shanxi and Xinzhou regional troupes. Eight or nine musicians were recruited to the band at first, gradually increasing to around sixteen; with singers, dancers, stage crew, and cadres, the troupe consisted of around sixty people. Its reputation was second only to the troupe in the provincial capital Taiyuan.
Li Qing now found himself accompanying stirring patriotic folk songs and short simple instrumental compositions in revolutionary style. As a household Daoist, he was a born musician, and effortlessly versatile. Apart from his old vocal liturgy and the “holy pieces” of the shengguan instrumental music, he knew a wide range of more folksy instrumental pieces played on procession and for the popular afternoon sequence, and he had the local opera repertoire in his blood.
Dancer Feng Yumei, also from Yanggao, arranged some of the earliest dance suites in folklore style, like “The Earth around the Yellow River” (Huanghe yifangtu), considered one of the earliest and best creations in the idiom. The troupe performed a new opera composed in Hubei, later made into a film.
Li Qing was the only Daoist in the troupe; the only other instrumentalist from Yanggao was the fine gujiang shawm player Shi Ming (1932–2003) from Wangguantun just northwest (see also my Ritual and music of north China: shawm bands in Shanxi, p.22). They remained lifelong friends. Shi Ming, already 27 sui, had an eye for the dancers, but they preferred the younger more eligible guys, like Li Kui himself! The troupe’s star soloist on the suona shawm was Yang Xixi from Xinzhou. Our friends ranked him alongside the nationally celebrated virtuoso Hu Tianquan, also a native of Xinzhou, mainly renowned for his sheng playing. Li Qing sometimes played Yang Xixi’s guanzi for fun.
As the only sheng player in the troupe, Li Qing accompanied Zhang Futian’s flute solos. Sometimes he played solos himself, accompanied on the accordion by one Ma Yun, over 50 sui in 1958. One solo that his colleagues recall was a Napoleonic Marche du Victoire (Kaixuan guilai), perhaps even the March from Aida. Imagine—Li Qing even performed a foreign piece! He played with feeling, and was infinitely adaptable. The conductor never criticized him; if he made the slightest error, he would correct it at once. Zhang Futian’s appraisal was still higher than that of the local Daoists: “He was a genius—the greatest musician I ever met.”

Li Qing (left) with fellow wind players Yang Xixi and Shi Ming, 1959.
No less impressive was Li Qing’s personality. Affable and generous, he had no temper. Even if he got ill, he never asked for leave. He earned a reputation for generosity and for smoothing over disputes in the troupe; his mere presence was enough to ease any tensions within the group. In a society where mutual suspicion was fostered and nasty rumours spread rapidly, he had no bad words for anyone, and bore no grudges. Folk musicians prided themselves on loyalty (yiqi).
The salary system was graded. Ordinary members got 25 kuai a month, most of the band 35 kuai. Relatively senior, Li Qing was soon considered an “old artist” (laoyiren), getting 45 kuai a month. The wind players and dancers got an extra 2 liang in rations.
During his time in the troupe Li Qing learned the modern system of notation called jianpu “simplified notation,” which uses the Arabic numerals 1 to 7 to represent the solfeggio pitches of Chinese gongche notation. [2] Though simple, it never caught on in the countryside; for the Daoists, traditional gongche remained in place as a means of learning the outline of the shengguan instrumental melodies, and they had no need of any notation at all to learn all the complex vocal hymns. The gongche solfeggio translates rather easily into numerical notation. The latter was used in the troupe to learn new pieces, but Shi Ming didn’t take to it, so Li Qing helped him learn them. Li Qing was to put this new skill to use from the 1980s when he used it to write scores of his Daoist repertoire.
For much of the year the troupe went on tour through the impoverished countryside, doing over a hundred performances a year. Apart from visits further afield in north China, they toured throughout north Shanxi, including Yanggao villages—mostly on foot, sometimes with horses and carts. Sometimes they slept in peasant homes, dispersed among several suitable families by the village brigade, or in the village school; or they put up a big tent. They took their own food, and stoves to cook it on. Li Qing didn’t smoke or drink, but the others drank laobaiganr liquor from a little flask; at first the troupe supplied them with packs of Happiness cigarettes, but later they were reduced to picking up fag-ends after a gig and rolling them into a new one. Their program was written in ink and stuck up as a poster. It was a tough life—Zhang Futian admits he got fed up with it.
Over these four years Li Qing was only able to go home once or twice a year for a couple of days, bringing only a bit of money, but no food. His wife, alone with four children to look after, never visited him in Datong. Li Manshan only went to see him once, in 1961; but soon after he arrived, Li Qing had to go off with the troupe to Harbin in northeast China to perform, so he could only go to the station with his father before taking a packed windowless bus back to Yanggao town and walking home from there.
For several generations the Li family’s exquisite sheng mouth-organs had been made by the Gao family in Gaoshantun near Upper Liangyuan. In 1961 Li Qing managed to get an invitation for the elderly master Gao Bin (1887–1967) to spend ten days with the troupe mending his various sheng, when Gao was really down on his luck; even the meager pickings in the troupe’s canteen probably saved his life.
Like many state work-units throughout China, the troupe was cut back in 1962, and Li Qing returned to his village early that spring. With such relocations, by 1963 some 84% of the Chinese population were living in the countryside—the highest proportion in the history of the People’s Republic. [3]
The troupe staggered on until it was disbanded in late 1962. Some of its members were recruited to the provincial song-and-dance troupe in Taiyuan, some of the Xinzhou contingent found work back home, while others like Li Qing and Shi Ming had to return home to their starving villages. Several of the performers went on to wider fame; dancer Feng Yumei 冯玉梅 became chair of the provincial dance association, and folksinger Xing Chouhua 刑丑花, from Xinzhou, gained national renown. The troupe reformed in 1964; soon, mainly using Western instruments for the revolutionary “model operas”, it was dominated by “educated youth” from Beijing, Tianjin, and Shanghai. But it disbanded again in 1968.
For a peasant like Li Qing to be chosen for the troupe was a great honor. His “black” class status was no barrier to being selected, and on his return his local prestige was even greater. But in volatile political times, assaults were not far away. If the economy hadn’t collapsed at this time, Li Qing might have continued in the state system; after the end of the Cultural Revolution, he might even have become a sheng professor at a conservatoire. Still, I am grateful that the troupe folded, and that the troupes or conservatoires never again summoned him. Had he secured a long-term state post, he would never have resumed his ritual practice, copied all those scriptures and scores, or taught the present generation.
* * *
If Li Qing’s repertoire in the troupe was new, and his long ritual tradition on hold, at least he was still playing the sheng there and receiving a handsome regular salary. Food supplies in the city were scant, even in state work units; but meanwhile back in Upper Liangyuan, people were desperate. In the absence of Li Qing there were still plenty of Daoists available; the senior Li Peiye, or Li Peisen (who had cannily absented himself from political scrutiny by moving to Yang Pagoda), could have still led bands if there were demand. But they were virtually inactive; not only had their instruments been confiscated, but people’s bellies were empty, and patrons had no strength to observe ritual proprieties.
Still, Li Qing’s return in 1962 coincided with a very brief ritual revival, with a retreat from the extremist policies of the disastrous Leap. Though very few domestic or temple rituals had been held for some years. Li Manshan recalls taking part in a ritual in 1963, commissioned at the home of an individual as a vow for recovering from illness. This was perhaps the last time they recited the Averting Calamity scriptures (Rangzai jing). Already by now they were mainly doing funerals, but Li Qing’s widow recalled that even then they were only able to do two or three a month. So there was less work in the early 1960s than now—there was still a serious famine, and however many deaths there were, people couldn’t afford to put on a grand funeral even if they had the energy.
However intermittent the Daoists’ appearances were during these years, Li Manshan sighs as he recalls how the villagers loved their grand rituals before the Cultural Revolution—in the days before TV and pop music. Even by the time of my visits in 1991 and 1992 there still wasn’t any singing outside the gate—that only began from 1993. In 1991 virtually the whole village seemed to turn out, crowding round respectfully (see my film, from 30.32). Li Qing’s sojourn in the troupe had added to his reputation as a Daoist and virtuous man; Li Manshan’s own repute is still based to a considerable degree on that of his father.
For the Li family Daoists’ ritual revival from the late 1970s, see here and here.
[1] For which see the Yanggao xianzhi (1993), p.468. Alas, links to Chinese websites cited in my book seem to have disappeared—watch this space.
[2] For gongche and cipher notation, see also my Folk music of China, pp.111–123; Plucking the winds, pp.245–246, 262–263.
[3] Cf. Friedman, Pickowicz, and Selden, Revolution, resistance, and reform in village China, p.19.